Introduction
Preparing for the ICSE Class 10 Physics board exam can feel overwhelming, especially when it comes to the Spectrum chapter. Many students struggle with concepts like dispersion of light, colour formation, and properties of different radiations. The good news? Practicing previous year questions is one of the best ways to strengthen your preparation.
In this article, we bring you important Spectrum questions from past ICSE exams along with clear, step-by-step answers to help you revise smarter.
Study materials related to chapter 6 Spectrum
| ☛ Class 10 Concise Physics Chapter 6 Spectrum Ex 6(A) Solutions |
| ☛ Class 10 Concise Physics Chapter 6 Spectrum Ex 6(B) Solutions |
| ☛ Class 10 Concise Physics Chapter 6 Spectrum Ex 6(C) Solutions |
| ☛ Class 10 Chapter 6 – Spectrum Notes |
ICSE Class 10 Physics – Spectrum: Previous Year Questions
Question 1
Why are infra-red radiations preferred over ordinary visible light for taking photo-graphs in fog? [ICSE 2007]
Answer:
Infrared radiations are preferred over visible light for taking photographs in fog because they can penetrate fog, mist, and smoke much better than ordinary light.
Question 2
(i) A particular type of high energy invisible electromagnetic rays help us to study the structure of crystals. Name these rays and give another important use of these rays.
(ii) How does the speed of light in glass change on increasing the wavelength of light? [ICSE 2007]
Answer:
(i) The high energy invisible electromagnetic rays used in the study of the structure of crystals are X-rays.
Other use: Medical imaging (X-ray photography)
(ii) In glass, the speed of light increases when the wavelength increases.
Question 3
What is meant by primary colours? Name the primary colours of light. [ICSE 2008]
Answer:
Primary colours are the basic colours of light that cannot be produced by mixing other colours, but by combining them in different proportions, we can obtain all other colours.
The three primary colours of light are:
- Red
- Green
- Blue
Question 4
(i) Why is white light considered to be polychromatic in nature?
(ii) Give the range of the wavelength of those electromagnetic waves which are visible to us. [ICSE 2009]
Answer:
(i) White light is called polychromatic because it is made up of many colours (violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red), each having a different wavelength.
(ii) Range of wavelength which are visible to us are 4000 Å to 8000 Å.
Question 5
How does the value of angle of deviation produced by a prism change with an increase in the:
(i) value of angle of incidence.
(ii) wave-length of incident light? [ICSE 2009]
Answer:
(i) When the angle of incidence increases angle of deviation first decreases till it reaches the value known as minimum deviation position. After that with the increase in angle of incidence angle of deviation also increases.
(ii) Angle of deviation decreases with increase in the wavelength of light, so angle of deviation is maximum for violet light and least for red light.
Question 6
Two parallel ray of Red and Violet travelling through air, meet the air glass boundary as shown in the given figure.
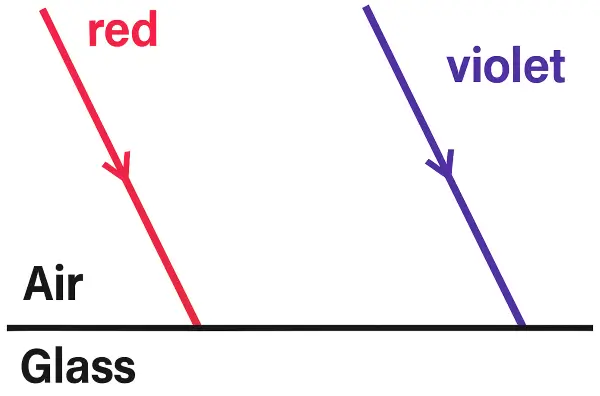
(i) Will their paths inside the glass be parallel? Give a reason for your answer.
(ii) Compare the speeds of the two rays inside the glass. [ICSE 2010]
Answer:
(i) No, their paths will not be parallel inside the glass.
Reason: Violet light has a shorter wavelength and is refracted more strongly than red light because the refractive index of glass is higher for violet than for red. Hence, the two rays will bend by different amounts and will not remain parallel.
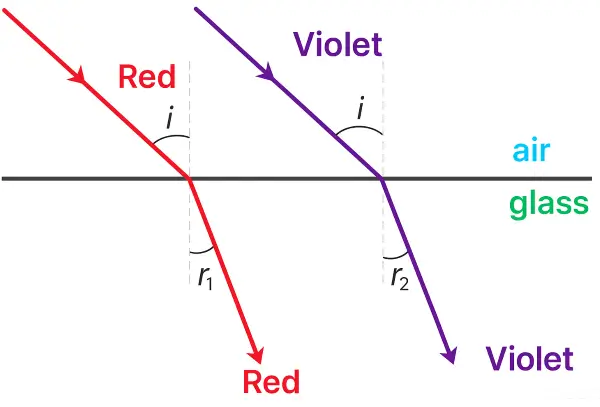
(ii) Red light travels faster in glass than violet light.
Question 7
Which characteristic property of light is responsible for the blue colour of the sky? [ICSE 2011]
Answer:
The characteristic property of light responsible for the blue colour of the sky is scattering of light.
Question 8
(i) Suggest one way, in each case, by which we can detect the presence of:
1. Infrared radiations
2. Ultraviolet radiations.
(ii) Give one use of Infrared radiations. [ICSE 2011]
Answer:
(i) Detection methods:
- Infrared radiations (IR): They can be detected by a thermopile or by observing the rise in temperature of a blackened thermometer when placed in the path of IR.
- Ultraviolet radiations (UV): They can be detected by the fluorescence they produce
(ii) One use of Infrared radiations: In remote controls for operating TV, AC, etc.
Question 9
(i) What is meant by ‘Dispersion of light’?
(ii) In the atmosphere which colour of light gets scattered the least? [ICSE 2012]
Answer:
(i) The phenomenon of splitting of white light of a prism into its constituent colours is called dispersion of light.
(ii) Red colour
Question 10
Name the radiations:
(i) That are used for photography at night.
(ii) Used for detection of fracture in bones.
(iii) Whose wavelength range is from \(100\ Å\) to \(4000\ Å\) (or 10 nm to 400 nm). [ICSE 2013]
Answer:
(i) Infrared radiations
(ii) X-rays
(iii) UV radiations
Question 11
(i) Name the high energetic invisible electromagnetic waves which help in the study of the structure of crystals.
(ii) State an additional use of the waves mentioned in part (i). [ICSE 2014]
Answer:
(i) The high energetic invisible electromagnetic waves used to study the structure of crystals are X-rays.
(ii) X-Ray are also used for detection fracture in bones.
Question 12
(i) Name a prism required for obtaining a spectrum of Ultraviolet light.
(ii) Name the radiations which can be detected by a thermopile. [ICSE 2014]
Answer:
(i) Quartz prism
(ii) Infrared radiations can be detected by thermopile.
Question 13
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger? [ICSE 2014]
Answer:
In the visible light, the wavelength of red light is longest, therefore the light of red colour is scattered least by the air molecules of the atmosphere.
Hence red light is used for danger signal, so that the signal may be visible from the far distance even in fog, etc.
Question 14
A type of electromagnetic wave has wavelength 50 Å.
(i) Name the wave.
(ii) What is the speed of the wave in vacuum?
(iii) State one use of this type of wave. [ICSE 2014]
Answer:
(i) X-Ray
(ii) \(3\times{10}^8\ m/s\)
(iii) X-Ray are used for detection fracture in bones.
Question 15
(i) Name the high energetic invisible electromagnetic waves which help in the study of the structure of crystals.
(ii) State an additional use of the waves mentioned in part (i). [ICSE 2015]
Answer:
(i) The high energetic invisible electromagnetic waves used to study the structure of crystals are X-rays.
(ii) X-Ray are also used for detection fracture in bones.
Question 16
(i) Why does the Sun appear red at sunrise?
(ii) Name the subjective property of light related to its wavelength. [ICSE 2015]
Answer:
(i) As sunlight travels a longer path through the atmosphere, most of the blue and green light gets scattered away. What finally reaches our eyes is mainly red and orange light.
As a result, the Sun and the region near by it, is seen red.
(ii) Colour is the subjective property of light related to its wavelength.
Question 17
What do you understand by the term ‘Scattering of light’? Which colour of white light is scattered the least and why? [ICSE 2016]
Answer:
Scattering of light:
The phenomenon of irregular reflection of light by the small particles suspended in a medium in all directions is called scattering of light.
The red colour of the white light is scattered the least because scattering of light depends inversely upon the four power of wavelength. As red colour has the maximum wavelength in the visible region, therefore, it scattered the least.
Question 18
(i) Define scattering.
(ii) The smoke from a fire looks white. Which of the following statements is true?
- Molecules of the smoke are bigger than the wavelength of light.
- Molecules of the smoke are smaller than the wavelength of light. [ICSE 2018]
Answer:
(i) The phenomenon of irregular reflection of light by the small particles suspended in a medium in all directions is called scattering of light.
(ii) The correct statement is:
1. Molecules of the smoke are bigger than the wavelength of light.
Question 19
(i) Why is the ratio of the velocities of light of wavelengths 4000 Å and 8000 Å in vacuum 1 : 1?
(ii) Which of the above wavelengths has a higher frequency? [ICSE 2018]
Answer:
(i) In vacuum the light of each wavelength travels with the same speed i.e., the speed of light of wavelength of 4000 Å is same as that of light of wavelength 8000 Å.
(ii) The light of wavelength 4000 Å will have higher frequency.
Question 20
An electromagnetic radiation is used for photography in fog.
(i) Identify the radiation.
(ii) Why is this radiation mentioned by you, ideal for this purpose? [ICSE 2019]
Answer:
(i) The radiation used for photography in fog is Infrared radiation.
(ii) Infrared has a longer wavelength, so it is scattered less by fog droplets and can penetrate fog better for photography.
Question 21
Give reasons for the following:
During the day:
(i) Clouds appear white.
(ii) Sky appears blue. [ICSE 2020]
Answer:
(i) Clouds appear white because water droplets scatter all colours of light equally.
(ii) Sky appears blue because air molecules scatter shorter wavelengths (blue) more than longer wavelengths.
Question 22
Choose the correct answer:
The wavelength range of visible light is : [ICSE 2021 Sem 1]
(a) 40 nm to 80 nm
(b) 4000 nm to 8000 nm
(c) 4 nm to 8 nm
(d) 400 nm to 800 nm
Answer:
(d) 400 nm to 800 nm
Question 23
Choose the correct answer:
The ratio of velocities of light of wavelength 400 nm and 800 nm in a vacuum is: [ICSE 2021 Sem 1]
(a) 1 : 1 (b) 1 : 2
(c) 2 : 1 (d) 1 : 3
Answer:
(a) 1 : 1
Question 24
The diagram below shows two parallel rays A (Orange) & B (Blue) incident from air, on air-glass boundary.
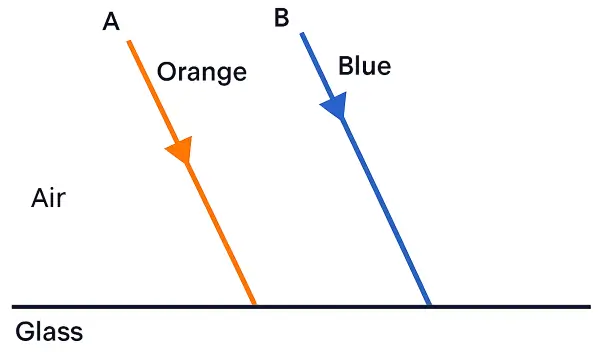
(a) Copy and complete the path of the rays A and B.
(b) How do the speeds of these rays differ in glass?
(c) Are the two refracted rays in glass parallel? Give a reason. [ICSE 2023]
Answer:
(a) Ray B (Blue) will bend more than ray A (Orange) as shown in the diagram below:
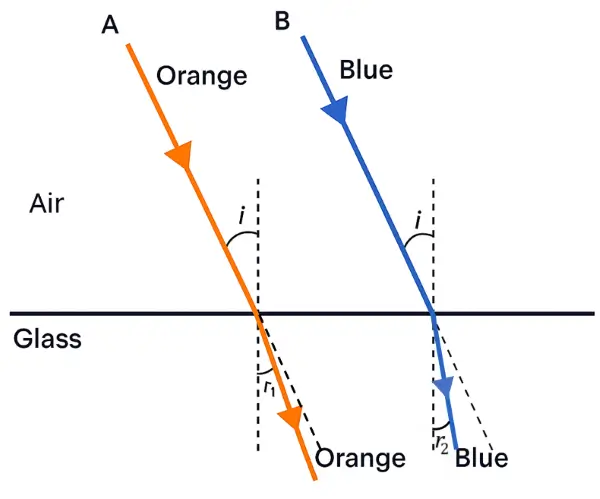
(b) In glass, speed of orange (A) light is more than that of blue light (B).
(c) The two refracted rays are not parallel in glass as orange light with more speed bends less while blue light with slow speed bends more.
Question 25
A ray of light is incident at 45° on an equilateral prism in the diagram below.
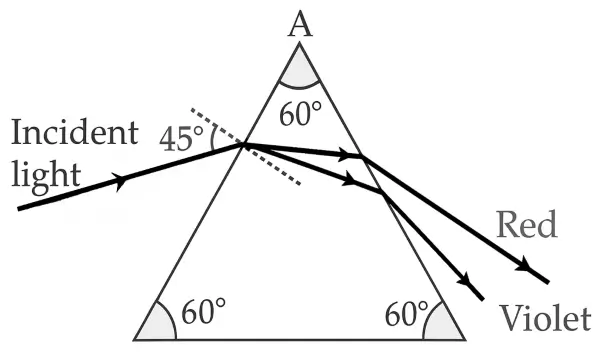
(i) Name the phenomenon exhibited by the ray of light when it enters and emerges out of the prism.
(ii) State the cause of the above phenomenon mentioned by you. [ICSE 2023]
Answer:
(i) When a ray enters the prism, it undergoes refraction and dispersion of light.
When the ray emerges from the prism, it undergoes refraction and deviation.
(ii) The above phenomena occur because the different colours of light travel with different speeds in the medium, causing them to bend by different amounts.
Question 26
Infrared radiations are used in warfare. Explain with reason, why. [ICSE 2023]
Answer:
Infrared radiations are used in warfare because they can penetrate fog and smoke and help in night-vision detection of warm objects.
Question 27
Choose the correct answer:
Assertion (A): Ultraviolet radiations are scattered more as compared to the microwave radiations.
Reason (R): Wavelength of ultraviolet radiation is more than the wavelength of microwave radiation. [ICSE 2024]
(a) Both A and R are true.
(b) A is true but R is false.
(c) A is false but R is true.
(d) Both A and R are false.
Answer:
(b) A is true but R is false.
Question 28
Below is an incomplete table showing the arrangement of electromagnetic spectrum in the increasing order of their wavelength. Complete the table. [ICSE 2024]
| Gamma ray | X-ray | U V rays | Visible rays | Infra- red | A | Radio waves |
(a) Identify the radiation A.
(b) Name the radiation used to detect fracture in bones.
(c) Name one property common to both A and Radio waves.
Answer:
(a) Radiation A : Micro Wave
(b) X – rays are used to detect fracture in bones.
(c) A common property is that both are transverse waves.
Question 29
Why do we use red colour as a danger signal on the top of a skyscraper? [ICSE 2024]
Answer:
Red colour is used as a danger signal on top of skyscrapers because it has the longest wavelength, is scattered the least by dust and fog, and can be seen clearly from a long distance.
Question 30
Choose the correct answer:
Which one of the following combinations is the correct ascending order of electromagnetic waves in terms of wavelength? [ICSE 2025]
(a) Gamma-rays, visible light, microwaves
(b) Microwaves, visible light, gamma-rays
(c) Gamma-rays, microwaves, visible light
(d) Microwaves, gamma-rays, visible light
Answer:
(a) Gamma-rays, visible light, microwaves
Question 31
(a) Name the radiations:
- for which a quartz prism is used to study the spectrum.
- which are used in remote sensing devices.
- which are used in traffic signals in India.
(b) Name one property common to all electromagnetic radiations. [ICSE 2025]
Answer:
(a) 1. Ultraviolet (UV) radiations
2. Infrared (IR) radiations
3. Visible light radiation (Red, Yellow, Green)
(b) They all travel with the speed of light in vacuum
Download Spectrum – Previous Year Questions PDF
You can download our free Spectrum – Previous Year Questions with answers (PDF format) to test your understanding.
Tips to Score High in Spectrum Chapter
- Practice ray diagrams (like dispersion through prism).
- Revise properties and uses of EM waves.
- Learn definitions in one line (e.g., scattering, wavelength).
- Solve sample papers & past year board questions.
You can also visit :
| ☛ ICSE Class 10 Physics |
| ☛ ICSE Class 10 Chemistry |
| ☛ ICSE Class 10 Mathematics |
ICSE Class 10 Physics Important Previous Year Questions
| ☛ Chapter 1 – Force Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 2 – Work, Energy and Power Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 3 – Machines Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 4 – Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 5 – Refraction through Lens Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 6 – Spectrum Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 7 – Sound Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 8 – Current Electricity Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 9 – Electrical Power and Household Circuits Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 10 – Electro-magnetism Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 11 – Calorimetry Previous Year Questions |
| ☛ Chapter 12 – Radioactivity Previous Year Questions |

