Introduction
If you are preparing for your ICSE Class 10 Physics exams, then practicing questions from Selina Solutions for Chapter 6: Spectrum is very important. Spectrum is one of the most crucial chapters in Physics, covering concepts like dispersion of light, visible spectrum, electromagnetic waves, and their applications. To help you prepare better, here are the step-by-step solutions for Spectrum Exercise 6(A) from Selina ICSE Physics Class 10.
(A) Multiple Choice Type
(Choose the correct answer from the options given below).
Question 1
When a white light ray falls on a prism, the ray at its first surface suffers :
(a) no refraction
(b) only dispersion
(c) only deviation
(d) both deviation and dispersion
Answer:
(d) both deviation and dispersion
Explanation:
When white light enters the first surface of a prism, the different colours travel at different speeds in glass and are therefore deviated by different angles toward the base of the prism. This causes the white light to split into its constituent colours, meaning both deviation and dispersion occur at the first surface.
Question 2
When a ray of white light falls on a prism, which of the following statements are correct ?
(a) The dispersion of white light occurs at the first surface of the prism.
(b) The deviation of light rays occurs at both the surfaces of the prism.
(c) The prism does not produce colours, but it only splits the various colours present in the white light.
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Explanation:
(i) Dispersion starts at the first surface.
(ii) Deviation happens at both surfaces.
(iii) A prism doesn’t create colours, it only separates those already in white light.
Question 3
The correct arrangement of colours in an increasing order of their wavelengths is :
(a) Violet < Green < Red
(b) Red < Green < Violet
(c) Green < Violet < Red
(d) Green < Red < Violet
Answer:
(a) Violet < Green < Red
Explanation:
In the visible spectrum, wavelength increases from violet to red. Violet has the shortest wavelength, green is intermediate, and red has the longest.
Question 4
Out of red, blue and violet, which colour has the greatest speed in vacuum ?
(a) red
(b) blue
(c) violet
(d) all have the same speed
Answer:
(d) all have the same speed
Explanation:
In a vacuum, all colours of light (red, blue, violet) travel at the same speed, which is the speed of light , as the speed of light is independent of wavelength in a vacuum.
Question 5
A beam consisting of red, blue and yellow colours is incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC as shown in the figure given below. Critical angle of glass-air interface for yellow colour is 45°.
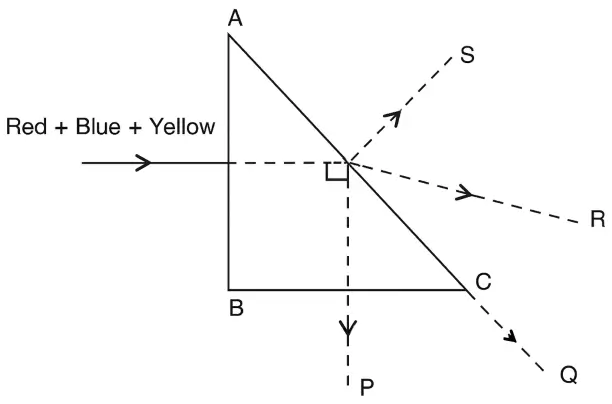
Out of the four emergent rays P, Q, R and S, which one is for the yellow colour :
(a) P (b) Q
(c) R (d) S
Answer:
(b) Q
Explanation:
As the critical angle for yellow colour is 45°, so it suffers refraction along the line AC of the prism.
Question 6
The frequency of violet light is 7.5 x 1014 Hz. Its wavelength in nm is :
(a) 7500 nm (b) 4000 nm
(c) 400 nm (d) 750 nm
Answer:
(c) 400 nm
Explanation:
Given,
Frequency range, \(f=\ 7.5\times{10}^{14}\ Hz\)
\(C=3\times{10}^8\ {ms}^{-1}\)
As we know,
Speed of light (c) = Frequency (f) x Wavelength (λ)
\(\Rightarrow 3\times{10}^8=\ 7.5\times{10}^{14}\ \times\lambda\)
\(\Rightarrow\ \lambda=\frac{3\times{10}^8}{7.5\times{10}^{14}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\ \lambda=0.4\times{10}^{-6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\ \lambda=400\times{10}^{-9}\ m\)
Therefore,
λ = 400 nm
Question 7
The correct order of angle of deviation of indigo, green, yellow and red colours is :
(a) \(\delta_I>\delta_G>\ \delta_Y>\delta_R\)
(b) \(\delta_G>\delta_I>\ \delta_Y>\delta_R\)
(c) \(\delta_R>\delta_G>\ \delta_Y>\delta_I\)
(d) \(\delta_R>\delta_Y>\ \delta_G>\delta_I\)
Answer:
(a) \(\delta_I>\delta_G>\ \delta_Y>\delta_R\)
Explanation:
The angle of deviation decreases with increasing wavelength. Indigo has the shortest wavelength, followed by green, yellow, and red (longest), so the deviation is highest for indigo and lowest for red.
Question 8
Assertion (A): When a ray of light is refracted through a rectangular glass slab, there is no dispersion of light.
Reason (R): Dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colours.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) assertion is false but reason is true
(d) assertion is true but reason is false.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
Explanation:
Assertion (A) is true: When a ray of light passes through a rectangular glass slab, there is no dispersion. After refraction at the two parallel faces of the slab, the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray. Since rays of all colours emerge in the same direction, there is no splitting of colours, only a lateral displacement.
Reason (R) is also true: Dispersion of light is the splitting of white light into its constituent colours. However, this definition does not explain the reason stated in the assertion.
Question 9
Assertion (A): A beam of white light gives a spectrum on passing through a hollow prism.
Reason (R): The speed of light outside the prism is same as the speed of light inside the prism.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) assertion is false but reason is true
(d) assertion is true but reason is false.
Answer:
(c) assertion is false but reason is true
Explanation:
A hollow prism does not produce a spectrum because there is no difference in refractive index between the inside and outside, so light passes without deviation or dispersion. The reason is correct in stating that the speed of light is the same inside and outside.
(B) Very Short Questions
Question 1
How does the speed of light in glass change on increasing the wavelength of light?
Answer:
The speed of light in glass increases as the wavelength increases.
Question 2
Which colour of white light travels (a) fastest (b) slowest, in glass?
Answer:
(a) Red (fastest)
(b) Violet (slowest)
Question 3
Name the subjective property of light related to its wavelength.
Answer:
Colour of light is the subjective property of light related to its wavelength.
Question 4
What is the range of wavelength of the spectrum of white light in :
(i) Å, and
(ii) nm?
Answer:
(i) The range of wavelength in Å is 4000 Å to 8000 Å.
(ii) The range of wavelength in nm is 400 nm to 800 nm.
Question 5
Name four colours of the spectrum of white light which have wavelength longer than blue light.
Answer:
Green, Yellow, Orange, Red
Question 6
How will the dispersion of light through a prism change if the prism is made of diamond instead of glass?
Answer:
Dispersion will increase because the refractive index of diamond is higher than that of glass, causing greater separation of colours.
(C) Short Questions
Question 1
Name three factors on which the deviation produced by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you.
Answer:
Factors affecting deviation by a prism :
(i) Angle of incidence (i): deviation first decreases, becomes minimum at the angle of minimum deviation, then increases as i increases.
(ii) Angle of prism (A): larger A gives larger deviation.
(iii) Refractive index / colour (μ or λ): higher μ (shorter wavelength) gives larger deviation.
Question 2
How does the deviation produced by a triangular prism depend on the colour (or wavelength) of light incident on it?
Answer:
The deviation of light in a prism depends on its wavelength: light with shorter wavelengths (like violet) bends more, while light with longer wavelengths (like red) bends less. So, the smaller the wavelength, the greater the bending.
Question 3
(a) Write the approximate wavelengths for (i) blue and (ii) red light.
(b) The wavelength of violet and red light are 4000 Å and 8000 Å respectively. Which of the two has higher frequency?
Answer:
(a) The approximate wavelengths for blue light is 4800 Å and red light is 8000 Å.
(b) Violet light of 4000 Å has higher frequency.
Question 4
Write the seven prominent colours present in white light in the order of increasing wavelength.
Answer:
Seven colours in order of increasing wavelength: Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red.
Question 5
Name the seven prominent colours of the white light spectrum in order of their increasing frequencies.
Answer:
Seven colours in order of increasing frequency: Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet
Question 6
The wavelengths for the light of red and blue colours are nearly \(7.8\times{10}^{-7}m\) and \(4.8\times{10}^{-7}m\) respectively.
(a) Which colour has the greater speed in vacuum?
(b) Which colour has greater speed in glass?
Answer:
(a) In vacuum, both have the same speed.
(b) In glass, red light has greater speed.
Question 7
Define the term dispersion of light.
Answer:
The phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colours, when it passes through a prism is called dispersion.
Question 8
What do you understand by the term spectrum?
Answer:
The bend of colours obtained on the screen by dispersion of white light is called spectrum. The 7 colours are VIBGYOR (Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red).
Question 9
A ray of white light is passed through a glass prism and a spectrum is obtained on a screen.
(a) Name the seven colours of the spectrum in order.
(b) Do the colours have the same width in the spectrum?
(c) Which colour of the spectrum of white light deviates (i) the most? (ii) the least?
Answer:
(a) The seven colours of the spectrum in order are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red.
(b) No, all the seven colours have different widths in the spectrum.
(c) Violet deviates the most; Red the least.
Question 10
How would the dispersion of light change if the prism is submerged in water instead of air ? Will the spread of the constituent colours remain the same ?
Answer:
When a prism is placed in water instead of air, the dispersion of light becomes smaller. This happens because dispersion depends on the difference in refractive index between the prism and the surrounding medium.
In air, this difference is large, so light bends more at the prism surfaces, producing greater dispersion. In water, the difference is less, so the bending of light at the surfaces is weaker. As a result, the separation between the constituent colours is reduced.
(D) Long Questions
Question 1
Explain the cause of dispersion of white light through a prism.
Answer:
When white light passes through a prism, it splits into a band of colours. This happens because each colour in white light bends by a different amount as it enters and leaves the prism. Violet light bends the most, and red bends the least. The reason behind this is that the glass of the prism slows down each colour by a slightly different amount, and that difference makes the light spread out into the spectrum.
Question 2
Explain briefly, with the help of a neat labelled diagram, how does white light gets dispersed by a prism. On which surface of the prism, there is both the dispersion and deviation of light, and on which surface of the prism, there is only the deviation of light?
Answer:
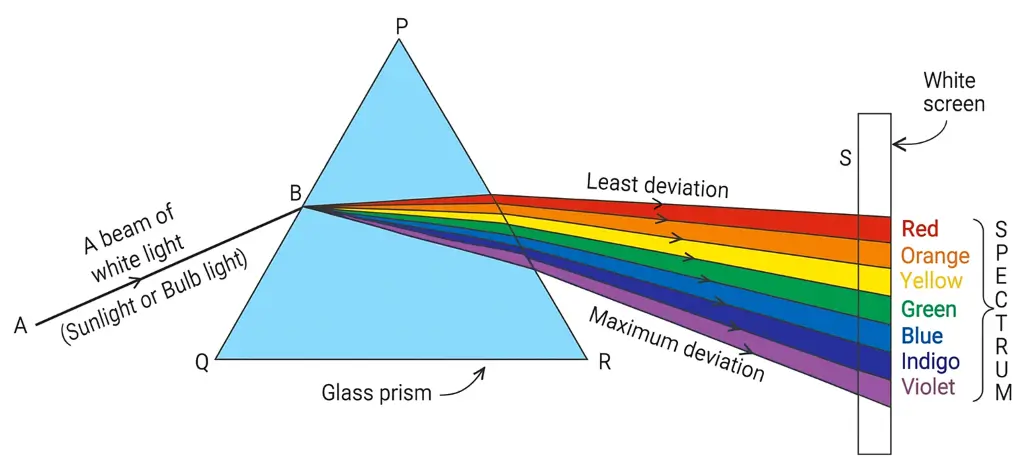
When a narrow beam of white light is passed through a glass prism, it splits into a band of seven colours, called the spectrum. This happens because the refractive index of glass is different for different colours of light. Violet light, having the shortest wavelength, bends the most, while red light, having the longest wavelength, bends the least. This unequal bending of different colours is called dispersion of light.
- At the first surface of the prism, when light enters from air to glass, both deviation and dispersion take place.
- At the second surface, when light comes out from glass to air, only deviation occurs.
Question 3
The diagram shown below, shows the path taken by a narrow beam of yellow monochromatic light passing through an equiangular glass prism. If the yellow light is replaced by a narrow beam of white light incident at the same angle, draw another diagram to show the passage of the white light through the prism and label it to show the effect of the prism on the white light.
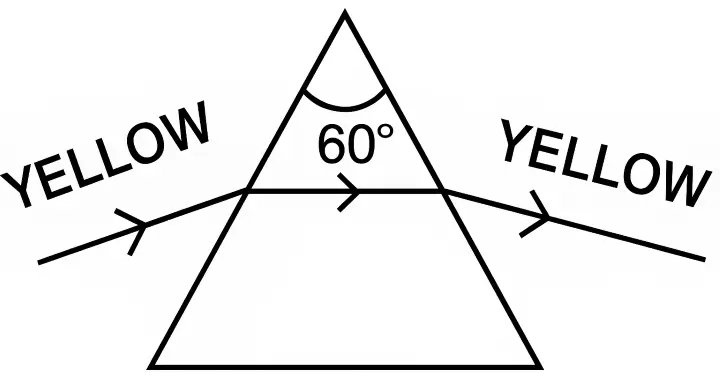
Answer:
Below diagram shows the effect of the prism on the white light:

Question 4
The figure given below, shows a thin beam of white light from a source S striking on one face of a prism.
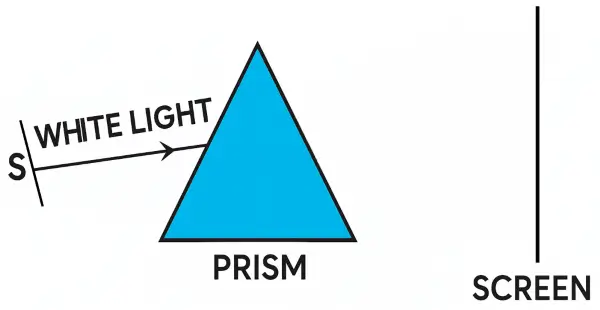
(a) Complete the diagram to show the effect of the prism on the beam and to show what is seen on the screen.
(b) If a slit is placed in between the prism and the screen to pass only the light of green colour, what will you then observe on the screen?
(c) What conclusion do you draw from the observation in part (b) above?
Answer:
(a) Below diagram shows the effect of the prism on the beam and the spectrum seen on the screen:

A coloured patch like a rainbow is seen on the screen. This is called the spectrum.
(b) If a slit is placed between the prism and the screen allowing only green light to pass, then only a single green patch will be seen on the screen, instead of the whole spectrum.
(c) From the above experiment, we can conclude that the prism does not create colours; it simply separates the different colours already present in the incident light.
Question 5
(a) A beam of monochromatic light undergoes minimum deviation through an equiangular prism. How does the beam pass through the prism, with respect to its base?
(b) If white light is used in the same way as in part (a) above, what change do you expect in the emergent beam?
(c) What conclusion do you draw about the nature of white light in part (b)?
Answer:
(a) At minimum deviation, the ray travels symmetrically through the prism, and the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to the base.
(b) With white light, the emergent beam splits into its colours. Violet deviates the most toward the base and red the least, so you get a small spectrum instead of a single beam.
(c) White light is polychromatic. It is a mixture of different wavelengths, which refract by different amounts in a prism.
(E) Numericals
Question 1
Calculate the frequency of yellow light of wavelength 550 nm. The speed of light is \(3\times{10}^8\ {ms}^{-1}\).
Answer:
Given,
\(\lambda\ =550\ nm\)
\(\lambda\ =\ 550\ \times\ {10}^{-9}\ m \left[\because\ {1\ nm=10}^{-9}\ m\right]\)
\(\lambda\ =\ 0.55\ \times\ {10}^{-6}\ m\)
\(C=3\times{10}^8\ {ms}^{-1}\)
We know that,
Speed of light (c) = Frequency (f) x Wavelength (λ)
\(\Rightarrow3\times{10}^8=f\times\ 0.55\ \times\ {10}^{-6}\)
\(\Rightarrow f=\frac{3\times{10}^8}{0.55\ \times\ {10}^{-6}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f=5.4\ \times{10}^{14}\ Hz\)
Hence,
Frequency of yellow light \(=5.4\ \times{10}^{14}\ Hz\)
Question 2
The frequency range of visible light is from \(3.75\ \times{10}^{14}\ Hz\) to \(7.5\ \times{10}^{14}\ Hz\). Calculate its wavelength range. Take speed of light \(=3\times{10}^8\ {ms}^{-1}\)
Answer:
Given,
\(C=3\times{10}^8\ {ms}^{-1}\)
\(f_1=3.75\ \times{10}^{14}\ Hz\)
We know that,
Speed of light (c) = Frequency (f) x Wavelength (λ)
\(\Rightarrow\ C=f_1\times\lambda_1\)
\(\Rightarrow\ 3\times{10}^8=3.75\ \times{10}^{14}\ \times\lambda_1\)
\({\Rightarrow\lambda}_1=\frac{3\ \times\ {10}^8}{3.75\ \times{10}^{14}}\)
\({\Rightarrow\lambda}_1=\ 8000\ \times\ {10}^{-10}m\)
\({\Rightarrow\lambda}_1=\ 8000\ Å \left[\because\ {1\ Å=10}^{-10}\ m\right]\)
Again,
Given,
\(f_2=7.5\ \times{10}^{14}\ Hz\)
We know that,
Speed of light (c) = Frequency (f) x Wavelength (λ)
\(\Rightarrow\ C=f_2\times\lambda_2\)
\(\Rightarrow\ 3\times{10}^8=7.5\ \times{10}^{14}\ \times\lambda_2\)
\({\Rightarrow\lambda}_2=\frac{3\ \times\ {10}^8}{7.5\ \times{10}^{14}}\)
\({\Rightarrow\lambda}_2=\ 0.4\ \times\ {10}^{-6}\ m\)
\({\Rightarrow\lambda}_2=\ 4000\ \times\ {10}^{-10}m\)
\({\Rightarrow\lambda}_2=\ 4000\ Å \left[\because\ {1\ Å=10}^{-10}\ m\right]\)
Therefore, the wavelength range is 4000 Å to 8000 Å.
Free PDF Download – Spectrum Exercise 6(A) Solutions
Students can Download ICSE Class 10 Physics Selina Solutions Chapter 6 Spectrum Exercise 6(A) PDF for offline practice. This is highly beneficial for last-minute revision before exams.
Why Use Selina Solutions for Spectrum?
- The ICSE Physics Selina Solutions provide accurate, exam-oriented answers.
- Exercise 6(A) Spectrum questions are explained in a simple and clear manner.
- Helps in solving previous year ICSE Physics Spectrum questions.
- Solutions are highly useful for revision and board exam preparation.

