Introduction
Searching for ICSE Class 10 Physics Selina Solutions Chapter 1 Force Ex 1C? You’re in the right place! Our Selina Concise Physics Class 10 Force Exercise 1C Solutions offer step-by-step answers to help you master uniform circular motion and centripetal force, key topics in Selina Physics Class 10 Chapter 1 Force. Designed for ICSE students, these solutions simplify complex concepts for quick revision and exam success. Download our free PDF to get started!
What is Covered in Selina Physics Class 10 Chapter 1 Force Exercise 1(C)?
Exercise 1(C) focuses on uniform circular motion and centripetal force, essential concepts in physics that explain how objects move in circular paths. Key topics include:
- Uniform Circular Motion: Motion of an object in a circle at a constant speed.
- Centripetal Force: The force that keeps an object moving in a circular path, directed toward the center.
- Examples: Real-world applications like a stone tied to a string or a car on a curved road.
- Numerical Problems: Calculations involving centripetal force and velocity.
Our ICSE Class 10 Force Selina Solutions Ex 1C break down these topics with clear explanations and exam-oriented answers.
Selina Questions and Solutions from Exercise 1(C)
Below are selina questions from Selina Concise Physics Class 10 Force Exercise 1C with concise solutions to kickstart your preparation:
(A) Multiple Choice Type : Exercise 1(C)
Question 1
Which of the following quantities remains constant in uniform circular motion?
(a) Velocity
(b) Speed
(c) Acceleration
(d) Both velocity and speed
Answer:
(b) Speed
Explanation: In uniform circular motion, only speed is constant; velocity changes due to the change in direction.
Question 2
The direction of motion in circular motion :
(a) is linear
(b) is along the tangent at that point of the circular path
(c) towards the centre
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) is along the tangent at that point of the circular path
Explanation: The instantaneous direction of motion in circular motion is tangential to the path.
Question 3
The direction of centripetal force is always :
(a) along the tangent at that point of the circular path
(b) towards the centre
(c) outwards from the centre
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) towards the centre
Explanation: Centripetal force is always directed towards the centre of the circular path.
Question 4
Centrifugal force is :
(a) a real force
(b) the force of reaction of centripetal force
(c) a fictitious force
(d) directed towards the centre of the circular path
Answer:
(c) a fictitious force
Explanation: Centrifugal force is an apparent or fictitious force observed in a rotating frame of reference.
Question 5
The difference between centrifugal force and centripetal force is :
(a) they both act in the same direction
(b) they both act in opposite direction
(c) they both have different magnitudes
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) they both act in opposite direction
Explanation: Centripetal force acts towards the centre; centrifugal (fictitious) force acts away from the centre.
Question 6
Which of the following is an example of uniform circular motion?
(a) a car accelerating on a straight road
(b) a pendulum swinging back and forth
(c) a satellite orbiting the earth at a constant altitude
(d) a ball rolling down a hill
Answer:
(c) a satellite orbiting the earth at a constant altitude
Explanation: This is uniform circular motion, where the speed is constant and the path is circular.
Question 7
Assertion (A) : When a beam is in static equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments is equal to the sum of anticlockwise moments.
Reason (R): According to the principle of moments for a body in equilibrium, the sum of moments acting in one direction must be equal to the sum of moments in opposite direction.
(a) both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) both A and R are True and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) assertion is false but reason is true
(d) assertion is true but reason is false
Answer:
(a) both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation:
This is the principle of moments — in static equilibrium, total clockwise moments = total anticlockwise moments. So, both A and R are true, and R explains A.
Question 8
Assertion (A) : A heavier object placed at a far distance from the pivot point will have the same moment as a lighter object placed close to the pivot point.
Reason (R) : The moment of force is determined by the magnitude of the force along with its distance from the pivot point.
(a) both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) both A and R are True and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) assertion is false but reason is true
(d) assertion is true but reason is false
Answer:
(c) assertion is false but reason is true
Explanation:
The moment is given by:
Moment = Force × Perpendicular distance
Question 9
Assertion (A) : The centre of gravity of an irregularly shaped object always lies at its geometric centre.
Reason (R) : The centre of gravity depends on the distribution of mass within an object.
(a) both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) both A and R are True and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) assertion is false but reason is true
(d) assertion is true but reason is false
Answer:
(c) assertion is false but reason is true
Explanation:
The centre of gravity of an irregular object does not always lie at its geometric centre.
However, the reason is true — it depends on mass distribution, not just shape.
(B) Very Short Questions : Exercise 1(C)
Question 1
Is it possible to have an accelerated motion with a constant speed? Name such type of motion.
Answer:
Yes, it is possible to have accelerated motion with a constant speed. This type of motion is called uniform circular motion.
Question 2
Give an example of motion in which speed remains uniform, but the velocity changes.
Answer:
An example of motion where speed remains uniform but velocity changes is uniform circular motion.
Motion of an artificial satellite around the Earth is a example of uniform circular motion.
Question 3
Name the force required for circular motion. State its direction.
Answer:
Centripetal force is required for circular motion. The centripetal force always acts towards the center of the circular path.
Question 4
Is centrifugal force a real force?
Answer:
No, centrifugal force is not a real force. It is a fictitious force.
Question 5
State whether the following statements are true or false by writing T/F against them.
(a) Earth moves around the Sun with a uniform velocity.
(b) The motion of Moon around Earth in a circular path is an accelerated motion.
(c) A uniform linear motion is unaccelerated, while a uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion.
(d) In a uniform circular motion, the speed continuously changes because the direction of the motion changes.
(e) A boy experiences a centrifugal force on his hand when he rotates a piece of stone tied at one end of a string, holding the other end in the hand.
Answer:
(a) False
(b) True
(c) True
(d) False
(e) False
(C) Short Questions : Exercise 1(C)
Question 1
Differentiate between uniform linear motion and a uniform circular motion.
Answer:
| Uniform Linear Motion | Uniform Circular Motion |
| The object moves along a straight path. | The object moves along a circular path. |
| Speed and direction both remains constant. | Speed is constant but direction changes continuously. |
| The velocity remains constant because both speed and direction are unchanging. | The velocity changes continuously because the direction of motion keeps changing as the object moves along the circle. |
| There is no acceleration since both speed and direction are constant. | Accelerated motion due to continuous change in velocity and direction. |
| Example: A car moving at constant speed on a straight road. | Example: Earth moves around the Sun with a uniform velocity. |
Question 2
What is a centripetal force
Answer:
Which force is required to move a body in a circular path with uniform speed, known as centripetal force. The direction of centripetal force is always directed towards the centre of the circle.
Question 3
Explain the motion of a planet around the Sun in an elliptical path.
Answer:
The motion of a planet around the Sun in an elliptical path is an example of uniform circular motion. The gravitational force of attraction on the planet by the Sun provides the necessary centripetal force for this uniform circular motion as it is always directed towards the centre of the Sun.
Question 4
(a) How does a centripetal force differ from a centrifugal force with reference to the direction in which they act?
(b) Is centrifugal force the force of reaction of the centripetal force?
(c) Compare the magnitudes of centripetal and centrifugal force.
Answer:
(a) Centripetal force acts towards the center of the circular path, while centrifugal force acts away from the center.
(b) No, centrifugal force is not the force of reaction of the centripetal force.
(c) The magnitude of the centripetal and the centrifugal force are equal but their direction are opposite to each other.
Question 5
State two differences between the centripetal and centrifugal force.
Answer:
| Centripetal force | Centrifugal force |
| Force acts towards the centre of the circle. | Force acts away from the centre of the circle. |
| A real force | A fictitious force |
(D) Long Questions : Exercise 1(C)
Question 1
Explain the meaning of uniform circular motion. Why is such motion said to be accelerated?
Answer:
When a body moves with a constant speed in a circular path, its motion is said to be in uniform circular motion.
Uniform circular motion is said to be accelerated as the velocity changes with continuous change in direction of motion.
Question 2
Draw a neat labelled diagram for a particle moving in a circular path with a constant speed. In your diagram show the direction of velocity at any instant.
Answer:
The below diagram shows a particle moving in a circular path with a constant speed and its direction of velocity:
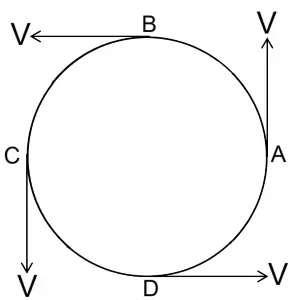
Question 3
A uniform circular motion is an accelerated motion. Explain it. State whether the acceleration is uniform or variable? Name the force responsible to cause this acceleration. What is the direction of force at any instant? Draw diagram in support of your answer.
Answer:
Uniform circular motion is accelerated motion because, although the speed remains constant, the direction of the velocity changes continuously, resulting in a centripetal acceleration that acts towards the center of the circle.
Centripetal force is required for this acceleration and its direction is towards the centre of the circular path.
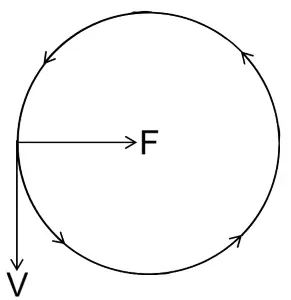
Question 4
A small pebble tied at one end of a string is placed near the periphery of a circular disc, at the center of which the other end of the string is tied to a peg. The disc is rotating about an axis passing through its centre.
(a) What will be your observation when you are standing outside the disc? Explain.
(b) What will be your observation when you are standing at the centre of the disc. Explain.
Answer:
(a) The pebble seems to move in a circular path when we are sitting outside the circular disc.
(b) The pebble seems to be stationary in front of us when we are standing at the centre of the disc.
Question 5
A piece of stone tied at the end of a thread is whirled in a horizontal circle with uniform speed with the help of hand.
Answer the following questions:
(a) Is the velocity of stone uniform or variable?
(b) Is the acceleration of stone uniform or variable?
(c) What is the direction of acceleration of stone at any instant?
(d) Which force provides the centripetal force required for circular motion?
(e) Name the force and its direction which acts on the hand.
Answer:
(a) Velocity of stone is variable.
(b) Acceleration of stone is variable.
(c) The acceleration is always directed towards the center of the circular path.
(d) The tension in the thread provides the necessary centripetal force.
(e) Centrifugal force acts on the hand and its direction is away from the centre.
Download Free ICSE Class 10 Force Exercise 1C Solutions PDF
Get your Selina Physics Class 10 Chapter 1 Force Ex 1C Answers in a free PDF format. Click below to download and boost your exam preparation!
Why Choose Our Selina Concise Physics Class 10 Ex 1C Solutions?
- Step-by-Step Answers: Detailed solutions for all questions in Exercise 1(C).
- Concept Clarity: Simplified explanations of uniform circular motion and centripetal force.
- Exam-Focused: Includes ICSE Class 10 Physics Uniform Circular Motion Questions and Answers with practice questions and MCQs.
- Free PDF Download: Access Selina Physics Class 10 Ex 1C Force Free PDF Download anytime.
- ICSE Syllabus-Aligned: Covers all topics tested in the board exams.
Tips to Master ICSE Class 10 Physics Chapter 1 Force Ex 1C
- Understand Key Concepts: Learn definitions of uniform circular motion and centripetal force.
- Practice Numericals: Solve problems like centripetal force calculations to build confidence.Use Examples: Relate concepts to real-life scenarios like vehicles on curves.
- Revise with Notes: Refer to our Selina Concise Physics Class 10 Uniform Circular Motion Notes for quick recaps.
- Test Yourself: Attempt ICSE Class 10 Physics Chapter 1 Force Ex 1C MCQs to evaluate your preparation.

