Introduction
Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces is one of the most important chapters in the ICSE Class 10 Physics syllabus. Every year, questions from this topic appear in the board exam, making it essential for students to practice previous year questions with answers. This article provides a complete set of important theory questions, solved numericals, and exam-focused tips to help you prepare effectively.
Why Focus on Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces?
In ICSE Class 10 Physics, the chapter covers key concepts such as laws of refraction, refractive index, apparent depth, lateral shift, and critical angle. Understanding these topics will not only help in scoring well in theory but also in solving important numericals on refraction.
Important Topics for ICSE Class 10 Refraction of Light
- Laws of Refraction
- Snell’s Law and Refractive Index
- Refraction through glass slabs
- Real and Apparent depth
- Lateral displacement
- Critical angle and total internal reflection
- Applications of refraction in daily life
Study materials related to chapter 4
ICSE Class 10 Physics – Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces: Previous Year Questions
Question 1
State Snell’s Law of Refraction of light. [ICSE 2007]
Answer:
The Snell’s laws of refraction of light are:
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence i to the sine of the angle of refraction r is constant for the pair of given media.
Question 2
Mention one difference between reflection of light from a plane mirror and total internal reflection of light from a prism. [ICSE 2007]
Answer:
| Plane mirror | Prism |
| In reflection of light from a plane mirror, only a part of the light is reflected while rest is refracted and absorbed. So, the reflection is partial. | In total internal reflection of light from a prism, the entire incident light is reflected back into the denser medium. So there is no loss of light energy. |
Question 3
The diagram given alongside shows a right angled prism with a ray of light incident on the side AB. (The critical angle for glass is 42°)

(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray of light in and out of the glass prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation shown by the ray? [ICSE 2007]
Answer:
(i) The required diagram is as shown in the fig.

(ii) The angle of deviation is 90°.
Question 4
(i) With the help of a well-labelled diagram show that the apparent depth of an object, such as a coin, in water is less than its real depth.
(ii) How is the refractive index of water related to the real depth and the apparent depth of a column of water? [ICSE 2007]
Answer:
(i)
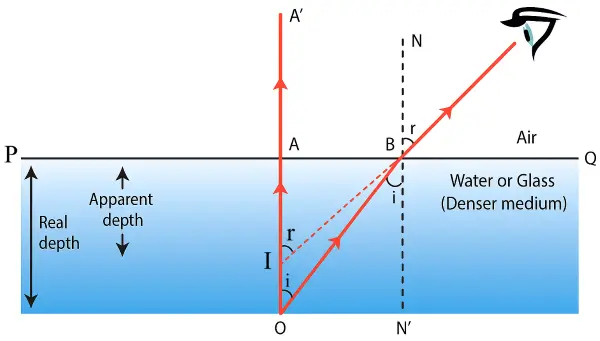
- AO = Real Depth
- AI = Apparent Depth
(ii) Relation between refractive index of water, real depth and apparent depth:
\(\mu=\frac{Real\ Depth\ }{Apparent\ Depth}\)
Question 5
(i) A monochromatic beam of light of wavelength X passes from air into a glass block. Write an expression to show the relation between the speed of light in air and the speed of light in glass.
(ii) As the ray of light passes from air to glass, state how the wavelength of light changes. Does it increase, decrease or remain constant? [ICSE 2008]
Answer:
(i) The relation between the speed of light in air c and in glass V is given by —
\(\mu=\frac{Speed\ of\ light\ in\ vacuum\ or\ air\ (c)}{Speed\ of\ light\ in\ that\ medium(V)}\)
(ii) As light passes from air to glass (a denser medium), the wavelength decreases.
Reason: Although the frequency remains constant, the speed of light decreases in the denser medium, which leads to a shorter wavelength.
Question 6
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate (1) critical angle (2) total internal reflection, for a ray of light moving from one medium to another.
(ii) Write a formula to express the relationship between refractive index of the denser medium with respect to rarer medium and its critical angle for that pair of media. [ICSE 2008]
Answer:
(i) (1) Critical Angle: When light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium, the critical angle is the angle of incidence for which the angle of refraction becomes 90°.
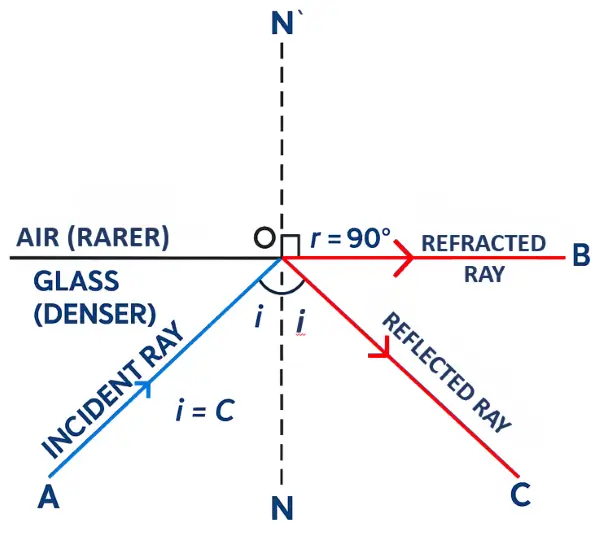
(2) Total Internal Reflection: If the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, the ray gets totally internally reflected back into the denser medium.
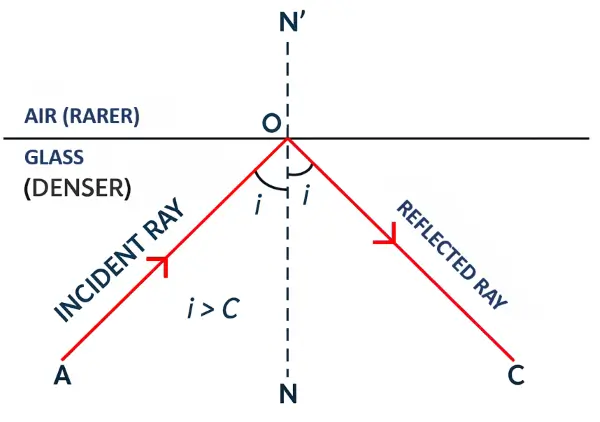
(ii) Formula for Refractive Index and Critical Angle:
\(\mu=\frac1{\sin\;C}\)
Question 7
Two isosceles right-angled glass prisms are placed near each other as shown in the figure.
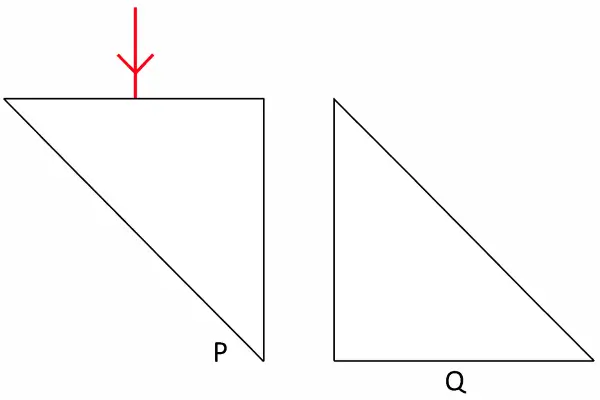
Complete the path of the light ray entering the first isosceles right-angled glass prism till it emerges from the second identical prism. [ICSE 2008]
Answer:
The diagram below shows the path of a light ray as it enters the prism at point P and emerges from the prism at point Q.
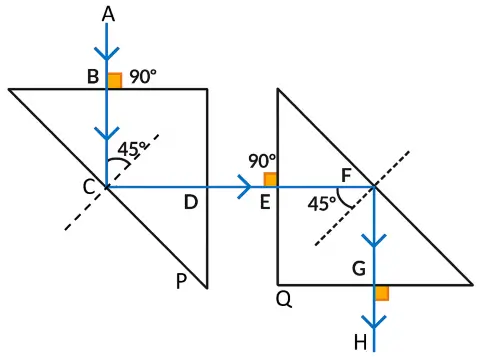
Question 8
(i) The diagram given alongside shows a ray of light incident on an equilateral glass prism placed in minimum deviation position. Copy the diagram and complete it to show the path of the refracted ray and the emergent ray.

(ii) How are angle of incidence and angle of emergence related to each other in this position of the prism? [ICSE 2008]
Answer:

In an equilateral prism, when the prism is in minimum deviation, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence .
Hence,
Angle of incidence (i1) = Angle of emergence (i2)
Question 9
State the conditions required for total internal reflection of light to take place. [ICSE 2009]
Answer:
The two necessary conditions for total internal reflection are —
(i) The light must travel from a denser medium to a rarer medium.
(ii) The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle for the pair of media.
Question 10
(i) The diagram given alongside shows a ray of white light PQ coming from an object P and incident on the surface of a thick glass plane mirror. Copy the diagram and complete it to show the formation of three images of the object P as formed by the mirror.

(ii) Which image will be the brightest image? [ICSE 2009]
Answer:
(i) The formation of three image is as shown below:

(ii) Image formed by P2 is brightest because it is formed by reflection as well as refraction.
Question 11
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass block such that the angle of incidence is (i) 0° (ii) 45°.
Sketch a diagram to show the approximate path taken by the ray in each case as it passes through the glass block and emerges from it. [ICSE 2009]
Answer:
(i) Below is the labelled diagram for ray of light at angle of incidence 0°:

(ii) Below is the labelled diagram for ray of light at angle of incidence 45°:

Question 12
(i) What is meant by refraction of light?
(ii) What is the cause of refraction of light? [ICSE 2010]
Answer:
(i) Refraction of light is the bending of a light ray when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent medium. This bending occurs due to a change in the speed of light.
(ii) The cause of refraction is the change in speed of light as it travels from one medium to another. When light travels from one medium to another with a different density, its speed changes, resulting in a change in its direction.
Question 13
‘The refractive index of diamond is 2.42’. What is meant by this statement? [ICSE 2010]
Answer:
The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. It means that light travels in air 2.42 times faster than in diamond.
OR,
It means that the speed of light in diamond is 2.42 times slower than its speed in vacuum or air.
Question 14
A ray of light enters a glass slab PQRS, as shown in the diagram. The critical angle of the glass is 42°. Copy this diagram and complete the path of the ray till it emerges from the glass slab.

Mark the angles in the diagram wherever necessary. [ICSE 2010]
Answer:
The diagram along with the complete path of ray is as shown below:

Question 15
A stick partly immersed in water appears to be bent. Draw a ray diagram to show the bending of the stick when placed in water and viewed obliquely from above. [ICSE 2010]
Answer:
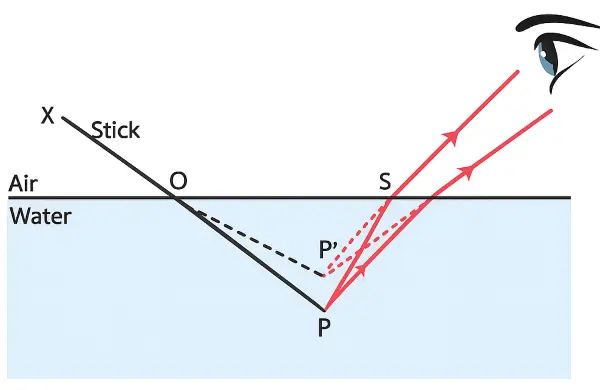
Question 16
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from air on a glass slab:
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the change in the path of the ray till it emerges from the glass slab.
(ii) Name the two rays that are parallel to each other.
(iii) Mark the lateral displacement in your diagram. [ICSE 2010]
Answer:
(i) The below diagram shows the path of the ray until it emerges out of the slab:

(ii) Incident ray and emergent rays are parallel to each other.
(iii) Lateral displacement is marked by CD in the diagram.
Question 17
A ray of monochromatic light enters a liquid from air as shown in the diagram given below:
(i) Copy the diagram and show in the diagram the path of the ray of light after it strikes the mirror and re-enters the medium of air.
(ii) Mark in your diagram the two angles on the surface of separation when the ray of light moves out from the liquid to air. [ICSE 2011]

Answer:
The diagram of the two angles on the surface of separation when the ray of light moves out from the liquid to air.

Question 18
In the diagram below, PQ is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray of light through the glass block. In your diagram, mark the angle of incidence by letter ‘i’ and the angle of emergence by the letter ‘e’.

(ii) How are the angle ‘i’ and ‘e’ related to each other? [ICSE 2011]
Answer:
(i) The below diagram shows the path of the ray until it emerges out of the slab:

(ii) Relation between angles i and e:
angle of incidence (i) = angle of emergence (e)
Question 19
How is the refractive index of a medium related to its real depth and apparent depth? [ICSE 2011]
Answer:
The refractive index is given by:
\(\mu=\frac{Real\ Depth\ }{Apparent\ Depth}\)
Question 20
(i) State the laws of refraction of light.
(ii) Write a relation between the angle of incidence (i), angle of emergence (e), angle of prism (A) and angle of deviation (δ) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism. [ICSE 2011]
Answer:
(i) The laws of refraction of light are:
- The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence i to the sine of the angle of refraction r is constant for the pair of given media.
(ii) \(A+\delta=i+e\)
Question 21
A ray of light incident at an angle of incidence V passes through an equilateral glass prism such that the refracted ray inside the prism is parallel to its base and emerges from the prism at an angle of emergence ‘e’.
(i) How is the angle of emergence ‘e’ related to the angle of incidence ‘i’?
(ii) What can you say about the value of the angle of deviation in such a situation? [ICSE 2012]
Answer:
(i) Angle of incident, ∠i = Angle of emergence, ∠e
(ii) The angle of deviation is the angle of minimum deviation.
Question 22
(i) What is meant by the term ‘critical angle’?
(ii) How is it related to the refractive index of the medium?
(iii) Does the depth of a tank of water appear to change or remain the same when viewed normally from above? [ICSE 2012]
Answer:
(i) The critical angle is the angle of incidence in a denser medium for which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium becomes 90°.
(ii) The critical angle is related to the refractive index by the relation:
\({}_a\mu_g=\frac1{\sin\;C}\), Where C in the critical angle.
(iii) The depth of a tank of water appears to remain the same when viewed normally (perpendicularly) from above.
Question 23
(i) Define the term refractive index of a medium in terms of velocity of light.
(ii) A ray of light moves from rare medium to a dense medium as shown in diagram below. Write down the number of the ray which represents the partially reflected ray. [ICSE 2012]

Answer:
(i) Refractive index of a medium is the ratio of velocity of light in vacuum or air to the velocity of light in a given medium.
\(\mu=\frac{Velocity\ of\ light\ in\ vacuum\ or\ air\ (c)}{Velocity\ of\ light\ in\ that\ medium\ (V)}\)
(ii) Ray 2, represents partially reflected ray.
Question 24
A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a A right angled prism ABC as shown in the diagram given below:
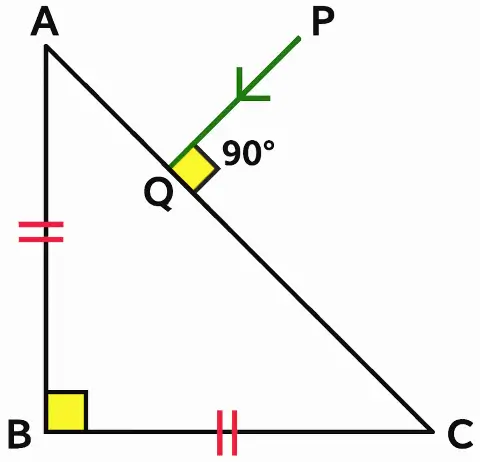
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
(iii) Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used. [ICSE 2012]
Answer:
(i) Below diagram shows the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism with all the angles labelled:
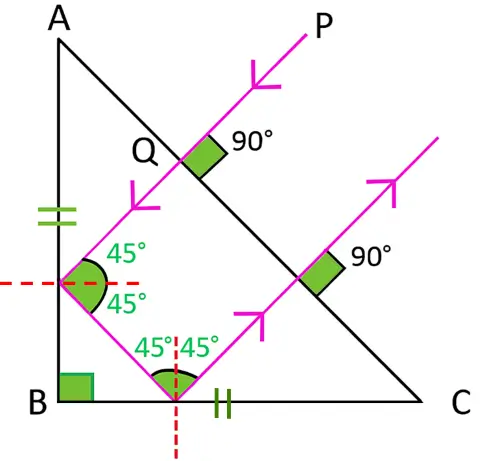
(ii) The angle of deviation of the ray PQ is 180°.
(iii) This action of the prism is used in Binoculars.
Question 25
(i) Can the absolute refractive index of a medium be less than one?
(ii) A coin placed at the bottom of a beaker appears to be raised by 4.0 cm. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the depth of the water in the beaker. [ICSE 2013]
Answer:
(i) No, the absolute refractive index of a medium cannot be less than one.
Given,
Refractive index of the glass block, \(\mu_g\ =\frac43\)
Shift in the image \(=\ 4\ cm\)
Thickness of glass block or real depth = ?
\(Shift\ =\ Real\ depth\ \times\left(1-\frac{1}{\mu}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow4\ =\ Real\ depth\ \times\left(1-\frac{3}{4}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow4\ =\ Real\ depth\ \times\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow Real\ depth=\ 4\times\ 4\)
\(\Rightarrow Real\ depth=\ 16\ cm\)
The depth of the water in the beaker is 16.0 cm.
Question 26
(i) The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 1.5. What is the value of the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
(ii) A ray of light is incident as a normal ray on the surface of separation of two different mediums. What is the value of the angle of incidence in this case? [ICSE 2013]
Answer:
(i) Refractive index of glass w.r.t air, \({{}_a\mu}_g=1.5\)
(ii) Refractive index of air w.r.t glass,
\({{}_g\mu}_a=\frac1{{{}_a\mu}_g}\)
\({{}_g\mu}_a=\frac1{1.5}=0.67\)
Hence, the refractive index of air with respect to glass is 0.67.
(ii) The angle of incidence is 0°.
Question 27
A ray of light is moving from a rarer medium to a denser medium and strikes a plane mirror placed at 90° to the direction of the ray as shown in the diagram.

(i) Copy the diagram and mark arrows to show the path of the ray of light after it is reflected from the mirror.
(ii) Name the principle you have used to mark the arrow to show the direction of the ray. [ICSE 2013]
Answer:
(i)

(ii) Principle of reversibility of light applied here.
Question 28
Draw the diagram given below and clearly show the path taken by the emergent ray. [ICSE 2014]

Answer:
Diagram of emergent ray:

Question 29
(i) A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
(ii) Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air? [ICSE 2014]
Answer:
(i) When a ray of light passes from water to air, the speed of light increases.
(ii) In any medium (except air), red light travels the fastest.
Question 30
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media. [ICSE 2014]
Answer:
The critical angle depends on two factors:
(i) The colour or wavelength of light : The refractive index of a transparent medium decreases with the increase of wavelength of light. (It is most for violet light and least for red light), therefore the critical angle for a pair of media is least for the violet light and most for the red light, i.e. the critical angle increases with the increase in wavelength of light.
(ii) The temperature : On increasing the temperature of medium, its refractive index decreases. So, the critical angle for the pair of medium increases with increase in temperature.
Question 31
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why? [ICSE 2014]
Answer:
For glass slab refer:

For prism refer:

In a rectangular glass slab, emergent light rays are always parallel to the incident rays. However, in a prism, the incident light bends toward the prism’s base, resulting in emergent rays that are not parallel to the incident rays.
Question 32
Name one factor that affects the lateral displacement of light as it passes through a rectangular glass slab. [ICSE 2015]
Answer:
One factor that affects the lateral displacement of light passing through a rectangular glass slab is the thickness of the slab.
The lateral displacement increases with the increase in the thickness of the glass slab.
Question 33
The speed of light in glass is \(2\times{10}^5\) km/s. What is the refractive index of glass? [ICSE 2015]
Answer:
Given,
Speed of light in glass \(=2\times{10}^5\ km/s\ =\ 2\times{10}^8\ m/s\)
Refractive index of glass is:
\(\mu_{glass}=\frac{3\times{10}^8}{2\times{10}^8}=1.5\)
Question 34
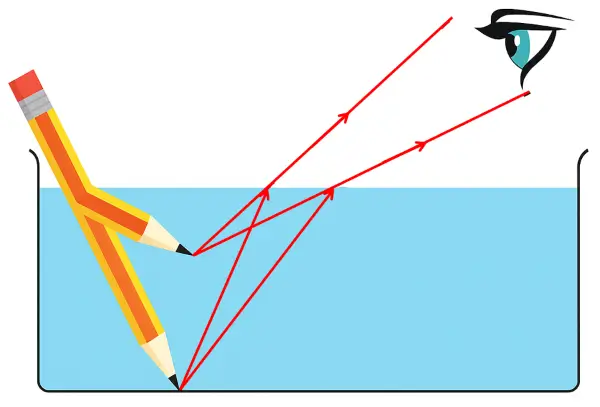
Jatin puts a pencil into a glass container having water and is surprised to see the pencil in a different state.
(i) What change is observed in the appearance of the pencil?
(ii) Name the phenomenon responsible for the change.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram showing how the eye sees the pencil. [ICSE 2015]
Answer:
(i) When water is poured into the trough, part of the pencil which is immersed in water will look short and raised up.
(ii) Refraction of light is responsible for the above observation.
(iii) The required diagram is shown below:
Question 35
A boy uses blue colour of light to find the refractive index of glass. He then repeats the experiment using red colour of light. Will the refractive index be the same or different in the two cases? Give a reason to support your answer. [ICSE 2016]
Answer:
The refractive index will be different in both cases. Refractive index of glass is different for different colours. The speed of blue light is less than the speed of red light. So, the wavelength of blue light is less than that of red light. Thus, red light would deviate less than blue light because of difference in wavelength.
Question 36
State the dependence of angle of deviation :
(i) On the refractive index of the material of the prism.
(ii) On the wavelength of light. [ICSE 2016]
Answer:
(i) Greater the refractive index, greater is the deviation produced.
(ii) Shorter wavelengths (like violet) are deviated more, and longer wavelengths (like red) are deviated less.
Question 37
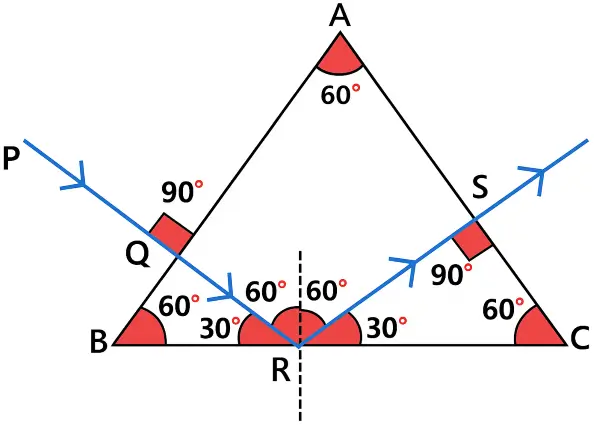
Copy the diagram given below and complete the path of light ray till it emerges out of the prism. The critical angle of glass is 42°. In your diagram mark the angles wherever necessary. [ICSE 2016]

Answer:
Completed diagram showing the path of the ray till it emerges out from the slab is shown below:
Question 38
(i) Write a relationship between angle of incidence and angle of refraction for a given pair of media.
(ii) When a ray of light enters from one medium to another having different optical densities it bends. Why does this phenomenon occur?
(iii) Write one condition where it does not bend when entering a medium of different optical density. [ICSE 2016]
Answer:
(i) Relationship between angle of incidence and angle of refraction for a given pair of media is given by Snell’s Law:
\(\mu=\frac{\sin\;i}{\sin\;r}\)
(ii) A ray of light bends when it enters from one medium to another of different optical density because its speed changes. This phenomenon is called refraction.
(iii) Light does not bend when it enters a medium of different optical density if it is incident normally (at 90°) to the surface.
Question 39
How is the refractive index of a material related to:
(i) real and apparent depth?
(ii) velocity of light in vacuum or air and the velocity of light in a given medium? [ICSE 2017]
Answer:
(i) Refractive index, \(\mu=\frac{Real\ depth}{Apparent\ depth}\)
(ii) Refractive index, \(\mu=\frac{Velocity\ of\ light\ in\ vacuum\ or\ air}{Velocity\ of\ light\ in\ medium}\)
Question 40
State the conditions required for total internal reflection of light to take place. [ICSE 2017]
Answer:
The conditions required for total internal reflection are:
(i) The light must travel from a denser medium to a rarer medium.
(ii) The angle of incidence of light in the denser medium must be greater than the critical angle for that pair of media.
Question 41
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic ray through a prism when it suffers minimum deviation. [ICSE 2017]
Answer:
Below diagram shows the refraction of a monochromatic light ray through a prism when it suffers minimum deviation:

Question 42
A ray of light travels from water to air as shown in the diagram given below :
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray. Given the critical angle for water is 48°.
(ii) State the condition so that total internal reflection occurs in the above diagram. [ICSE 2017]

Answer:
(i) A ray of light travels from water to air as shown in the diagram given below:

(ii) For total internal reflection to occur in the above diagram, the angle of incidence must be greater than 48°.
Question 43
The diagram below shows a point source P inside a water container. Four rays A, B, C, D starting from the source P are shown upto the water surface.

(i) Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface. The critical angle for water air surface is 48°.
(ii) Name the phenomenon which the rays B and D exhibit. [ICSE 2017]
Answer:
(i) Path of rays after striking the water surface is shown below:

(ii) The ray B exhibits the phenomenon of refraction.
The ray D exhibits the phenomenon of total internal reflection.
Question 44
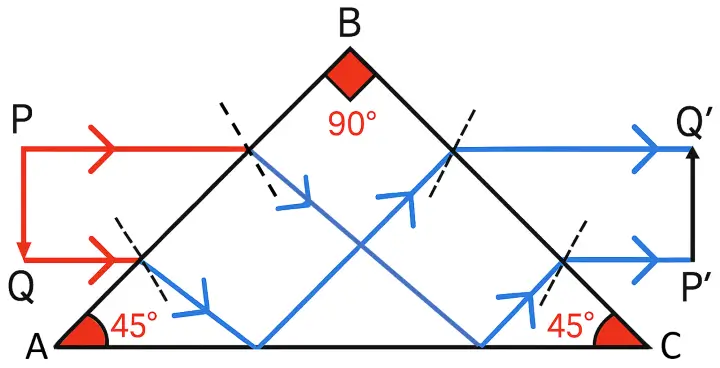
Draw the diagram of a right angled isosceles prism which is used erect. [ICSE 2018]
Answer:
Below is the diagram of a right angled isosceles prism which is used to make an inverted image erect:
Question 45
(i) State the relation between the critical angle and the absolute refractive index of a medium.
(ii) Which colour of light has a higher critical angle? Red light or Green light. [ICSE 2018]
Answer:
(i) \(\mu=\frac{1}{sin\ C}\) or \(sin\ C\ =\ \frac{1}{\mu}\)
where ‘c’ is critical angle and ‘μ’ is absolute refractive index.
(ii) Critical angle for ‘Red ‘ colour is higher.
Question 46
The following diagram shows a 60°, 30°, 90° glass prism of critical angle 42°. Copy the diagram and complete the path of incident ray AB emerging out of the prism marking the angle of incidence on each surface. [ICSE 2018]

Answer:
The completed diagram is given below:

Question 47
A ray of light XY passes through a right angled isosceles prism as shown below:
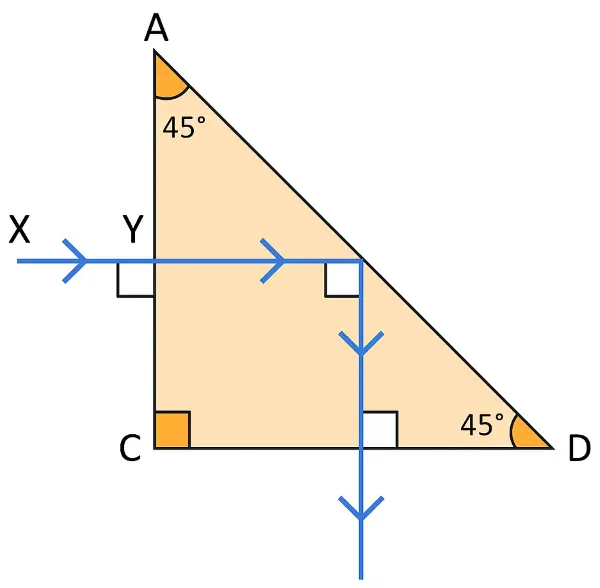
(i) What is the angle through which the incident ray deviates and emerges out of the prism?
(ii) Name the instrument where this action of prism is put into use.
(iii) Which prism surface will behave as mirror? [ICSE 2018]
Answer:
(i) Direction of the ray is perpendicular to the initial direction, the total deviation = 90°.
(ii) The instrument where this action of prism is put into use is the periscope.
(iii) Surface AB acts like a mirror due to Total Internal Reflection.
Question 48
(i) Define critical angle.
(ii) State one important factor which affects the critical angle of a given medium. [ICSE 2019]
Answer:
(i) The critical angle is the angle of incidence in a denser medium for which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium becomes 90°.
(ii) The refractive index of the medium affects the critical angle of a given medium.
Question 49
(i) What is the relation between the refractive index of water with respect to air (aμw) and the refractive index of air with respect to water (wμa)
(ii) If the refractive index of water with respect to air (aμw) is 5/3. Calculate the refractive index of air with respect to water (wμa). [ICSE 2019]
Answer:
(i) aμw = 1/wμa
(ii) aμw = 5/3
wμa = 3/5
Question 50
The diagram below shows a light source P embedded in a rectangular glass block ABCD of critical angle 42°. Complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges out of the block. [Write necessary angles. [ICSE 2019]

Answer:
The path of ray is as shown:

Question 51
How does the angle of deviation formed by a prism change with the increase in the angle of incidence?
Draw a graph showing the variation in the angle of deviation with the angle of incidence at a prism surface. [ICSE 2019]
Answer:
As the angle of incidence increases the angle of deviation decreases becomes minimum and then increases.
The graph is as shown :

Question 52
A ray of light falls normally on a rectangular glass slab. Draw a ray diagram showing the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab. [ICSE 2020]
Answer:
Below is the labelled diagram for ray of light at angle of incidence 0°:

Question 53
Complete the path of the monochromatic light ray AB incident on the surface PQ of the equilateral glass prism PQR till it emerges out of the prism due to refraction. [ICSE 2020]

Answer:
Below ray diagram shows the path of ray AB till it emerges out of the prism:

Question 54
A pond appears to be 2.7 m deep. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the actual depth of the pond. [ICSE 2020]
Answer:
Given,
Apparent depth \(=\ 2.7\ m\)
Refractive index of water, μw \(=\frac{4}{3}\)
We know that,
Real depth = Apparent depth × μw
Real depth \(=2.7\times\frac{4}{3}\)
Real depth \(=\ 3.6\ m\)
Hence, Actual depth of the pond \(=\ 3.6\ m\)
Question 55
The wave lengths for the light of red and blue colours are nearly \({7.8\times10}^{-7}\ m\) and \({4.8\times10}^{-7}\ m\) respectively.
(i) Which colour has the greater speed in a vacuum?
(ii) Which colour has a greater speed in glass? [ICSE 2020]
Answer:
(i) Both red and blue light have equal speed in a vacuum.
(ii) Red light has greater speed than blue light in glass.
Question 56
A diver in water looks obliquely at an object AB in air.

(i) Does the object appear taller, shorter or of the same size to the diver?
(ii) Show the path of two rays AC & AD starting from the tip of the object as it travels towards the diver in water and hence obtain the image of the object. [ICSE 2020]
Answer:
(i) The object appears taller to the diver.
(ii) Below diagram shows the path of two rays AC & AD:

Question 57
Complete the path of the ray AB through the glass prism in PQR till it emerges out of the prism. Given the critical angle of the glass as 42°. [ICSE 2020]

Answer:
Below diagram shows the path of ray PQ through the glass prism ABC till it emerges out of the prism:

Question 58
Choose the correct answer:
The deviation produced by an equilateral prism does not depend on [ICSE 2021 Sem 1]
(a) the angle of incidence.
(b) the size of the prism.
(c) the material of the prism.
(d) the colour of light used.
Answer:
(b) the size of the prism.
Explanation:
Angle of deviation depends on:
- Angle of incidence
- Refractive index
- Angle of the prism
Question 59
Choose the correct answer:
The refractive index of a diamond is 2.4. It means that: [ICSE 2021 Sem 1]
(a) the speed of light in vacuum is equal to 2.4 times the speed of light in diamond.
(b) the speed of light in the diamond is 2.4 times the speed of light in a vacuum.
(c) the speed of light in a vacuum is 2.4 times the speed of light in the diamond.
(d) the wavelength of light in diamond is 2.4 times the wavelength of light in vacuum.
Answer:
(c) the speed of light in a vacuum is 2.4 times the speed of light in the diamond.
Explanation:
Refractive index, \(\mu=\frac{Speed\ of\ light\ in\ vacuum,\ \ \ C}{Speed\ of\ light\ in\ the\ medium,\ V}\)
\(2.4=\frac{c}{V}\)
\(c=2.4V\)
This means the speed of light in vacuum is 2.4 times faster than in the diamond.
Question 60
Choose the correct answer:
A ray of light IM is incident on a glass slab ABCD as shown in the figure below. The emergent ray for this incident ray is [ICSE 2021 Sem 1]

(a) NQ (b) NR
(c) NP (d) NS
Answer:
(a) NQ
Explanation:
In a rectangular glass slab, the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray due to lateral displacement.
In the diagram, NQ is parallel to IM, so it’s the correct emergent ray.
Question 61
Choose the correct answer:
The colour of white light which is deviated least by a prism is [ICSE 2021 Sem 1]
(a) green (b) yellow
(c) red (d) violet
Answer: (c) red
Explanation:
Deviation depends on the refractive index, which is least for red light (longer wavelength). So red bends the least in a prism, while violet bends the most.
Question 62
Choose the correct answer:
The diagram below shows a ray of light travelling from air into a glass material as shown below. Answer the questions that follow: [ICSE 2021 Sem 1]

(i) The angle of incidence at the surface AB is
(a) 43° (b) 47°
(c) 90° (d) 0°
Answer:
(b) 47°
Explanation:
The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal at the surface where the light enters.
Hence, Angle of incidence = 90° – 43° = 47°.
(ii) Select a correct statement from the following.
(a) The speed of light at the curved surface AD does not change while entering the block.
(b) The ray at the surface AD is not travelling along the radius of the curved part.
(c) The ray at the surface AD is travelling along the radius of the curved part.
(d) Light never refracts when it enters a curved surface.
Answer:
(c) The ray at the surface AD is travelling along the radius of the curved part.
Explanation:
When a ray of light travels along the radius of a curved surface, it meets the surface perpendicularly (at 90° to the tangent). This means the angle of incidence is zero, so the ray passes through the surface without getting refracted.
(iii) The angle of incidence on the surface BC is [ICSE 2021 Sem 1]
(a) 43° (b) 47°
(c) 90° (d) 0°
Answer:
(a) 43°
Explanation:
Total internal reflection has occurred at F.
So, ∠EFB = 43°
So, ∠FEB = 90° – 43° = 47°
So, the angle of incidence at BC surface
= 90° – 47° = 43°
(iv) The critical angle of this material of glass
(a) 47° (b) 43°
(c) 42° (d) 45°
Answer:
(b) 43°
Explanation:
As we can see from the given figure, when angle of incidence at surface BC is 43° the light ray becomes parallel to surface BC. Hence for the given case the angle of incidence is 43°.
Question 63
Choose the correct answer:
The diagram below shows the path of light passing through a right-angled prism of critical angle 42°. [ICSE 2021 Sem 1]

(i) The angle C of the prism is
(a) 45° (b) 60°
(c) 90° (d) 30°
Answer:
(d) 30°
Explanation:
Since, angle of incidence > critical angle, total
internal reflection will occur at D.
∠ADE = 90° – 60° = 30°
∴ ∠A = 60°
Now in the triangle ABC,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
Or, 60° + 90° + ∠C = 180° ∴ ∠C = 30°
(ii) Which one of the following diagrams shows the correct path of this ray till it emerges out of the prism?


Answer:

Explanation:
The ray enters the prism and hits the face BC at an angle of 60° (greater than the critical angle 42°). Hence, Total Internal Reflection (TIR) occurs.
Only option (b) shows the ray reflecting completely from BC and emerging correctly from face AC.
Question 64
Choose the correct answer:
Speed of blue light in water is: [ICSE 2023]
(a) more than green light
(b) more than orange light
(c) more than violet light
(d) more than red light
Answer:
(c) more than violet light
Explanation:
The speed of light in a medium depends on its wavelength — light with a longer wavelength travels faster in materials like water or glass because it bends less during refraction.
Question 65
Choose the correct answer:
When a ray of light travels normal to the given surface, then the angle of refraction is: [ICSE 2023]
(a) 180° (b) 90°
(c) 0° (d) 45°
Answer:
(c) 0°
Explanation:
When a ray of light travels normally (i.e., perpendicular or at 0° incidence) to the surface of a medium, it does not bend. Since there is no deviation, the angle of refraction is 0°.
Question 66
Choose the correct answer:
Small air bubbles rising up a fish tank appear silvery when viewed from some particular angle is due to the: [ICSE 2023]
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) dispersion
(d) total internal reflection
Answer:
(d) total internal reflection
Explanation:
Small air bubbles in water appear silvery when viewed from certain angles because of total internal reflection (TIR).
Question 67
The diagram below shows the ray OP travelling through an equilateral prism of a certain material. [ICSE 2023]
(a) Calculate the value of i2, if the angle of deviation is 43°.
(b) What is the ray QS called?

Answer:
(a) Deviation, \(\delta=i_1+i_2-A\)
Or, \(43^\circ=65^\circ+i_2-60^\circ\)
∴ \(i_2=38^\circ\)
(b) QS is called emergent ray.
Question 68
Copy the diagram given below and complete the path of the light ray PQ, as it emerges out of the prism by marking necessary angles. The critical angle of glass is 42°. [ICSE 2023]
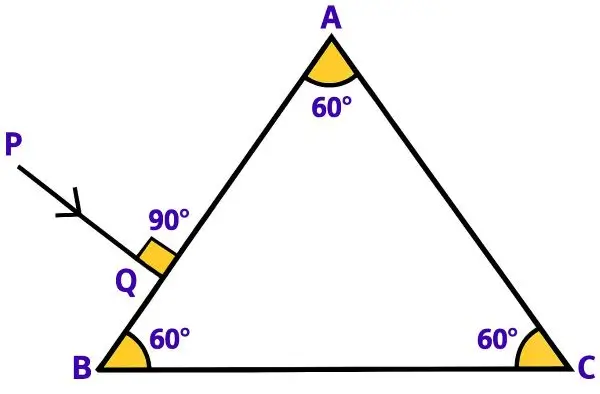
Answer:
Below is the completed diagram showing the path of the light ray till it emerges out of the prism with all angles marked:

Question 69
The diagram below shows two parallel rays A (Orange) & B (Blue) incident from air, on air-glass boundary. [ICSE 2023]
(a) Copy and complete the path of the rays A and B.
(b) How do the speeds of these rays differ in glass?
(c) Are the two refracted rays in glass parallel? Give a reason.

Answer:
(a) Ray B (Blue) will bend more than ray A (Orange) as shown in the diagram below:

(b) In glass, speed of orange (A) light is more than that of blue light (B).
(c) The two refracted rays are not parallel in glass as orange light with more speed bends less while blue light with slow speed bends more.
Question 70
(i) A coin kept inside water [µ=4/3 ] when viewed from air in a vertical direction appears to be raised by 3.0 mm. Find the depth of the coin in water.
(ii) How is the critical angle related to the refractive index of a medium? [ICSE 2023]
Answer:
(i) Given,
Refractive index of the glass block, μw \(=\frac{4}{3}\)
Shift \(=3\ mm\)
Depth of coin in water = ?
\(Shift\ =\ Real\ depth\ \times\left(1-\frac{1}{\mu}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3\ =\ Real\ depth\ \times\left(1-\frac{3}{4}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3\ =\ Real\ depth\ \times\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow Real\ depth=\ 3\times\ 4\)
\(\Rightarrow Real\ depth=\ 12\ mm\)
∴ Depth of coin in water = 12 mm
(ii) \(\mu=\frac{1}{sin\ C}\) or \(sin\ C\ =\ \frac{1}{\mu}\)
where ‘c’ is critical angle and ‘μ’ is absolute refractive index.
Question 71
The diagram below shows the path of a blue ray through the prism:
(i) Calculate the critical angle of the material of the prism for blue colour.
(ii) What is the measure of the angle of this prism (A)?
(iii) Which colour should replace the blue ray, for the ray to undergo Total Internal Reflection? [ICSE 2024]

Answer:
(i) The angle of refraction inside the prism at face AC is C = 90° – 47° = 43°, because angle of emergence is, and the angle of incidence inside the prism is complementary to it.
So, Critical angle, C = 43°

(ii) In ΔAPQ
∠APQ + ∠PQA + ∠PAQ = 180°
90° + 47° + ∠PAQ = 180°
∠PAQ = 180° – 90° – 47°
∠PAQ = 43°
∴ ∠A = 43°
∴ Angle of prism, ∠A = 43°
(iii) Replacing blue with violet or indigo causes total internal reflection due to their smaller critical angles.
Question 72
(i) Refractive index of glass with respect to water is \(\frac98\) . Find the refractive index of water with respect to glass.
(ii) Name the principle used to find the value in part (i).
(iii) If we change the temperature of water, then will the ratio 9/8 remain the same? Write Yes or No. [ICSE 2024]
Answer:
(i) Refractive index of glass with respect to water \(=\frac{9}{8}\)
Hence, Refractive index of water with respect to glass \(=\frac{8}{9}\)
(ii) Principle of reversibility of light is used here.
(ii) No, because refractive index depends on temperature—changing the temperature of water changes its optical density.
Question 73
Light travels a distance of ‘\(10x\)’ units in time ‘\(t_1\)’ in vacuum and it travels a distance of ‘\(x\)’ units in time ‘\(t_2\)’ in a denser medium. Using this information answer the question that follows:
(i) ‘Light covers a distance of ‘\(10x\)’ units in time ‘\(t_1\)’ in diamond. ‘State true or false
(ii) Calculate the refractive index of the medium in terms of ‘\(t_1\)’ and ‘\(t_2\)’. [ICSE 2024]
Answer:
(i) False
Explanation:
Speed of light in vacuum, \(c=\frac{10x}{t_1}\)
Speed of light in diamond, \(v=\frac{20x}{t_2}\)
Diamond is a denser medium than vacuum, so light must travel slower in diamond, not faster.
Since \(\frac{20x}{t_2}\ >\frac{10x}{t_1}\), it is not possible for light to cover ‘\(20x\)’ units in ‘\(t_1\)’ in diamond.
In diamond, which is a denser medium, light slows down further — so it would cover less distance than in vacuum for same time.
(ii) Speed of light in vacuum, \(c=\frac{10x}{t_1}\)
Speed of light in the denser medium, \(v=\frac{20x}{t_2}\)
The refractive index of the medium, \(\mu=\frac{c}{V}\)
\(\mu=\frac{\displaystyle\frac{10x}{t_1}}{\displaystyle\frac x{t_2}}=\frac{10x}{t_1}\times\frac{t_2}x=\frac{10t_2}{t_1}\)
Question 74
A monochromatic ray of light is incident on an equilateral prism placed at minimum deviation position with an angle of incidence 45° as shown in the diagram.

(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ.
(ii) State two factors on which the angle of deviation depends. [ICSE 2024]
Answer:
(i)

(ii) Two factors on which the angle of deviation depends are:
- Angle of incidence
- Refractive index of the prism
Question 75
Choose the correct answer:
A ray of light is incident normally on a face of an equilateral prism. The ray gets totally reflected at the second refracting surface. The total deviation produced in the path of the ray is: [ICSE 2025]
(a) 30° (b) 60°
(c) 90° (d) 120°
Answer:
(b) 60°
Explanation:
∠NRS = 60˚
∴ ∠SRC = 30˚
∠ARQ = 30˚
∴ ∠CRT = 30˚
RT is the original path of the incident ray.
So, total deviation = ∠SRT = 30˚ + 30˚ = 60˚
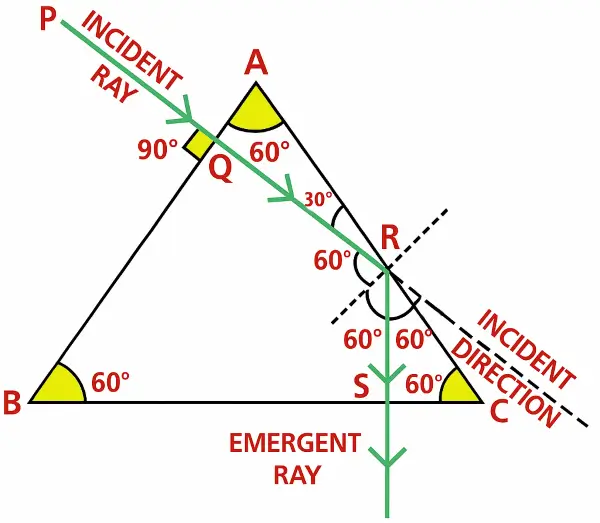
Question 76
A ray of light enters a rectangular glass slab submerged in water at an angle of incidence 55°. Does this ray undergo total internal reflection when it moves from water to glass? Justify your answer. (The critical angle for glass–water interface is 54°) [ICSE 2025]
Answer:
No, the ray does not undergo total internal reflection when it moves from water to glass.
In this case, the ray is traveling from water (a rarer medium) to glass (a denser medium).
Total internal reflection cannot take place when light moves from a rarer to a denser medium.
Question 77
(i) Out of the three rays (I, J, H) shown in the diagram, which ray will suffer Total Internal Reflection while inside the prism? (Critical angle of the prism is 42°.)
(ii) Copy the diagram to complete the path of the ray which you have named in (a) till it comes out of the prism. [ICSE 2025]

Answer:
(i) Ray J suffers Total Internal Reflection.
Explanation:

Inside the prism, the angles of incidence for rays I, J, and H are 30°, 60°, and 30° respectively. Since only ray J has an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle (42°), it alone will undergo total internal reflection.
(ii)

Question 78
A rectangular glass block of refractive index 1.5 has an air bubble trapped inside it as shown in the diagram. When seen from the surface AB, it appears to be 4 cm deep.

(i) Calculate the actual depth of the air bubble from the surface AB.
(ii) For which colour of light, blue or yellow, the apparent depth will be greater?
(iii) Turning the glass block upside down, DOES NOT change the apparent depth of the air bubble. State True or False. [ICSE 2025]
Answer:
(i) Refractive index of glass, μ = 1.5
Apparent depth = 4 cm
We know that,
Refractive index \(=\frac{Real\ depth}{Apparent\ depth}\)
or, \(1.5=\frac{Real\ depth\ }{4}\)
∴ Real depth = 6 cm
(ii) Apparent depth is greater for yellow light.
Explanation:
Apparent depth increases when the refractive index decreases.
As the wavelength of light increases, its refractive index decreases.
Yellow light has a longer wavelength than blue light.
Therefore, the refractive index for yellow light is less than that for blue light.
Hence, the apparent depth will be greater for yellow light.
(iii) False
Explanation:
When the block is turned upside down, then the real depth of the bubble is 15 – 6 = 9 cm
Refractive index \(=\frac{Real\ depth}{Apparent\ depth}\)
Or, \(1.5==\frac{9}{Apparent\ depth}\)
∴ Apparent depth \(=\frac{9}{1.5}=6\ cm\)
Question 79
Two rays PQ and RS are incident on a rectangular glass block as shown in the diagram. Observe the diagram and answer the questions that follow.

Which of these two rays will:
(i) have greater lateral displacement on emerging out of the block?
(ii) travel with greater speed in the block?
(iii) scatter more in the atmosphere? [ICSE 2025]
Answer:
(i) Ray RS will have greater lateral displacement.
Explanation:

Since the angle of incidence is the same for both rays, their directions remain unchanged. However, the refracted ray corresponding to RS bends more towards the normal than that of PQ. Therefore, the lateral displacement of the emergent ray corresponding to incident ray RS will be greater.
(ii) Ray PQ travels with greater speed.
Explanation:
Since RS likely has a shorter wavelength (blue/violet), it has a higher refractive index and therefore travels more slowly in glass.
On the other hand, ray PQ, with a longer wavelength (red/orange), has a lower refractive index and thus travels faster in glass.
(iii) Ray RS will scatter more in atmosphere.
Explanation:
The speed of the incident ray PQ is greater than that of the incident ray RS.
Therefore, the wavelength of the incident ray PQ is also greater than the wavelength of the incident ray RS.
So, Ray RS will scatter more in atmosphere.
Download Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces – Previous Year Questions PDF
You can download our free Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces – Previous Year Questions with answers (PDF format) to test your understanding.
How to Prepare for ICSE Physics Chapter 4
- Go through the ICSE Class 10 Physics solved question paper for the past 5–10 years.
- Practice both theory and numerical problems regularly.
- Revise important formulas related to refractive index and apparent depth.
- Solve ICSE Physics question bank Class 10 Refraction of Light for extra practice.
Final Tip
Mastering Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces ICSE solutions will give you an edge in the board exam. Focus on concepts, practice important previous year questions, and check your answers against the marking scheme to improve accuracy.
You can also visit :
| ICSE Class 10 Physics |
| ICSE Class 10 Chemistry |
| ICSE Class 10 Mathematics |
ICSE Class 10 Physics Important Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 2 – Work, Energy and Power Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 3 – Machines Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 4 – Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 5 – Refraction through Lens Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 6 – Spectrum Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 7 – Sound Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 8 – Current Electricity Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 9 – Electrical Power and Household Circuits Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 10 – Electro-magnetism Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 11 – Calorimetry Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 12 – Radioactivity Previous Year Questions