Introduction
Are you preparing for the ICSE Class 10 board exams? The Force chapter is one of the most important topics in Physics. It includes key concepts like moment of force, equilibrium, and levers – all frequently asked in exams. Here’s a compiled list of previous years’ questions, categorized for easy revision.
Study materials related to chapter 1
| Class 10 Chapter 1 Force Ex 1(A) Solutions |
| Class 10 Chapter 1 Force Ex 1(B) Solutions |
| Class 10 Chapter 1 Force Ex 1(C) Solutions |
| Class 10 Chapter 1 – Force Notes |
ICSE Class 10 Physics – Force: Previous Year Questions
Question 1
A man can open a nut by applying a force of \(150\ N\) by using a lever handle of length \(0.4\ m\). What should be the length of the handle if he is able to open it by applying a force of \(60\ N\)? [ICSE 2011]
Answer:
Given,
\(F_1\ =\ 150\ N\)
\(l_1\ =\ 0.4\ m\)
\(F_2\ =\ 60\ N\)
\(l_2\ =\ ?\)
Force x perpendicular distance = constant
\(F_1 \times l_1\ =\ F_2 \times l_2\)
\(150 \times 0.4\ =\ 60 \times l_2\)
\(l_2\ =\ 1\ m\)
Therefore, The handle should be \(1.0\ meter\) long.
Question 2
Where does the position of centre of gravity lie for
(i) a circular lamina
(ii) a triangular lamina? [ICSE 2011]
Answer:
(i) Triangular Lamina: The center of gravity is at the centroid, where the medians intersect.
(ii) Circular Lamina: The center of gravity is at the geometric center of the circle.
Question 3
A uniform metre scale can be balanced at the \(70.0\ cm\) mark when a mass of \(0.05\ kg\) is hung from the \(94.0\ cm\) mark.
(i) Draw a diagram of the arrangement.
(ii) Find the mass of the metre scale. [ICSE 2011]
Answer:
(i) Diagram of the given arrangement is shown below:

(ii) Let the mass of the meter-scale be \(w_1\ kg\).
From the principle of moments,
Anticlockwise moment \(=\) clockwise moment
\(w_1 \times (70\ −\ 50)\ =\ 0.05 \times (94\ −\ 70)\)
\(w_1 \times 20\ =\ 0.05 \times 24\ =\ 0.06\ kg\ =\ 60\ gm\)
Therefore, the mass of the meter scale is \(60\ gm\).
Question 4
A boy of mass \(30\ kg\) is sitting at a distance of \(2\ m\) from the middle of a see-saw. Where should a boy of mass \(40\ kg\) sit so as to balance the see-saw? [ICSE 2012]
Answer:
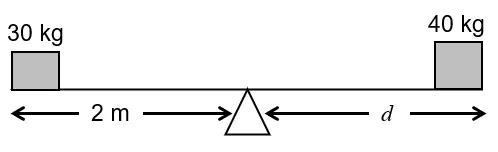
Mass of first boy \(=\ 30\ kg\)
Distance from pivot \(=\ 2\ m\)
Let the second boy \((40\ kg)\) sit at a distance \(‘d’\) from the pivot on the other side.
From principal of moment,
Moment of first boy \(=\) Moment of second boy
\(30 \times 20\ =\ 40 \times d\)
The \(40\ kg\) boy should sit \(1.5\ meters\) from the middle of the see-saw on the opposite side.
Question 5
(i) What is meant by the term ‘moment of force’?
(ii) If the moment of force is assigned a negative sign then will the turning tendency of the force be clockwise or anticlockwise? [ICSE 2012]
Answer:
(i) The moment of a force is the product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force.
Moment of force \(=\) Force × perpendicular distance
(ii) If the moment of force is assigned a negative sign, then the turning tendency of the force is clockwise.
Question 6
(i) Which of the following remains constant in uniform circular motion : Speed or Velocity or both?
(ii) Name the force required for uniform circular motion. State its direction. [ICSE 2012]
Answer:
(i) Speed remains constant in uniform circular motion.
(ii) The force required for uniform circular motion is centripetal force.
It is always directed towards the center of the circular path.
Question 7
(i) Where is the centre of gravity of a uniform ring situated?
(ii) “The position of the centre of gravity of a body remains unchanged even when the body is deformed.” State whether the statement is true or false. [ICSE 2013]
Answer:
(i) The centre of gravity of a uniform ring is situated at its geometrical centre.
(ii) False
Reason: The position of the centre of gravity can change if the shape or mass distribution of the body changes due to deformation.
Question 8
With reference to their direction of action, how does a centripetal force differ from a centrifugal force? [ICSE 2013]
Answer:
Centripetal force acts towards the center of the circular path, while centrifugal force acts away from the center.
Question 9
Two forces each of \(5\ N\) act vertically upwards and downwards respectively on the two ends of a uniform metre rule which is placed at its mid-point as shown in the diagram. Determine the magnitude of the resultant moment of these forces about the midpoint. [ICSE 2014]
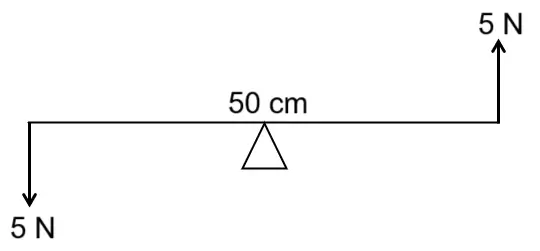
Answer:
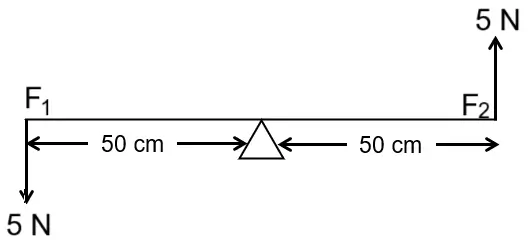
Given,
\(F_1\ =\ 5\ N\)
\(d_1\ =\ 25\ cm\ =\ 0.25\ m\)
\(F_2\ =\ 5\ N\)
\(d_2\ =\ 25\ cm\ =\ 0.25\ m\)
Moment of force, \(\tau_1\ =\ F_1 \times d_1\ =\ 5\ N \times 0.25\ m\ =\ 2.5\ Nm\) (anticlockwise direction)
Moment of force, \(\tau_2\ =\ F_2 \times d_2\ =\ 5\ N \times 0.25\ m\ = 2.5\ Nm\) (anticlockwise direction)
Resultant moment of force \(=\ 2.5\ Nm\ +\ 2.5\ Nm\ =\ 5\ Nm\) (anticlockwise direction)
Question 10
Is it possible to have an accelerated motion with a constant speed ? Explain. [ICSE 2014]
Answer:
Yes, it is possible to have accelerated motion with constant speed.
For example, in uniform circular motion the magnitude of speed is constant but direction of motion changes so that acceleration is produced.
Question 11
(i) On what factor does the position of the centre of gravity of a body depend?
(ii) What is the S.I. unit of the moment of force? [ICSE 2015]
Answer:
(i) The position of the centre of gravity of any body will depend on the shape or distribution of mass of the body. It changes if the shape of the body is deformed.
(ii) The S.I. unit of moment of force is Newton metre (Nm).
Question 12
Name the factors affecting the turning effect of a body. [ICSE 2015]
Answer:
Two factors affecting the turning effect of a force are:
(i) Magnitude of the force applied
(ii) Perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation
Question 13
(i) Define equilibrium.
(ii) In a beam balance when the beam is balanced in a horizontal position, it is in ……….. equilibrium. [ICSE 2015]
Answer:
(i) When several forces acting on a body produce no change in its state of rest or of linear or rotational motion, the body is said to be in equilibrium.
(ii) In beam balance when the beam is balanced in a horizontal position, it is in static equilibrium.
Question 14
A nut is opened by a wrench of length \(20\ cm\). If the least force required is \(2\ N\), find the moment of force needed to loosen the nut. [ICSE 2015]
Answer:
Given,
Force, \(F\ =\ 2\ N\)
Length of wrench, \(𝑑\ =\ 20\ 𝑐𝑚\ = \frac{20}{100} 𝑚\ =\ 0.2\ 𝑚\)
We know that,
\(Moment\ of\ force\ =\ Force \times perpendicular\ distance\ =\ 2 \times 0.2\ =\ 0.4\ Nm\)
Hence, moment of force needed to loosen the nut is \(0.4\ Nm\).
Question 15
A stone of mass \(‘m’\) is rotated in a circular path with a uniform speed by tying a strong string with the help of your hand. Answer the following questions :
(i) Is the stone moving with a uniform or variable speed?
(ii) Is the stone moving with a uniform acceleration? In which direction does the acceleration act?
(iii) What kind of force acts on the hand and state its direction? [ICSE 2016]
Answer:
(i) The stone is moving with a uniform speed.
(ii) Yes, the stone is moving with uniform (constant) acceleration. The direction of acceleration is towards the center.
(iii) The force acting on the hand is the centrifugal force. Its direction is away from the center of the circular path.
Question 16
Why is a jack screw provided with a long arm? [ICSE 2017]
Answer:
A jack screw used to lift a heavy vehicle is designed with a long arm so that it requires less force to rotate and raise or lower the vehicle.
Question 17
A uniform half metre rule balances horizontally on a knife edge at \(29\ cm\) mark when a weight of \(20\ gf\) is suspended from one end.
(i) Draw a diagram of the arrangement
(ii) What is the weight of the half metre rule? [ICSE 2017]
Answer:
(i)
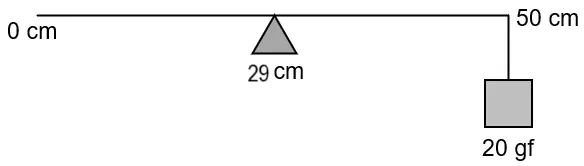
(ii) Let the mass of the meter-scale be \(w_1\ gm\).
From the principle of moments,
Anticlockwise moment \(=\) clockwise moment
\(⇒\ w_1 \times l_1\ =\ w_2 \times l_2\)
\(⇒\ w_1 \times (29\ −\ 25)\ =\ 20\ gf \times (50\ −\ 29)\)
\(⇒\ w_1\ = \frac{21\ \times\ 20}{4}\ =\ 105\ gf\)
The weight of half the meter rule is \(105\ gf\).
Question 18
How does uniform circular motion differ from uniform linear motion? [ICSE 2017]
Answer:
Uniform linear motion has constant speed and direction, while uniform circular motion has constant speed but changing direction.
Question 19
A half metre rod is pivoted at the centre with two weights of \(20\ gf\) and \(12\ gf\) suspended at a perpendicular distance of \(6\ cm\) and \(10\ cm\) from the pivot respectively as shown below:
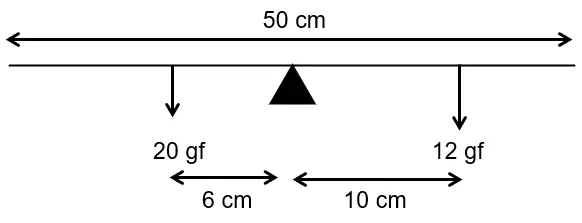
(i) Which of the two forces acting on the rigid rod causes clockwise moment?
(ii) Is the rod in equilibrium?
(ii) The direction of \(20\ gf\) force is reversed. What is the magnitude of the resultant moment of the forces on the rod? [ICSE 2018]
Answer:
The force \(12\ gf\) rotates the rod clockwise.
Clockwise moment \(=\ 20\ gf\ \times\ 6\ cm\ =\ 120\ gf\ cm\)
anticlockwise moment \(=\ 12\ gf\ \times\ 10\ cm\ =\ 120\ gf\ cm\)
Since, the clockwise moment is equal to the anticlockwise moment, hence the rod is in equilibrium.
total clockwise moment \(=\) Clockwise moment + anticlockwise moment
\(=\ 120\ gf\ cm\ +\ 120\ gf\ cm\ =\ 240\ gf\ cm\)
Question 20
Why is the motion of a body moving with a constant speed around a circular path said to be accelerated? [ICSE 2018]
Answer:
The motion of a body which is moving with constant speed in a circular path is said to be accelerated because its velocity changes continuously due to the continuous change in the direction of motion.
Question 21
(i) Define couple.
(ii) State the SI unit of moment of couple. [ICSE 2019]
Answer:
(i) Moment of couple: Moment of couple is product of either force and the perpendicular distance between the two forces.
(ii) S.I. unit of couple is Newton meter (Nm).
Question 22
A uniform metre scale is in equilibrium as shown in the diagram:
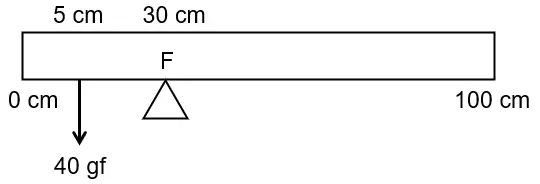
(i) Calculate the weight of the metre scale.
(ii) Which of the following options is correct to keep the ruler in equilibrium when \(40\ gf\ wt\) is shifted to \(0\ cm\) mark? \(F\) is shifted towards \(0\ cm\) or \(F\) is shifted towards \(100\ cm\). [ICSE 2019]
Answer:
(i) Let the mass of the meter-scale be W gf. From the principle of moments,
Anticlockwise moment \(=\) clockwise moment
\(⇒\ 40\ \times\ (30\ −\ 5)\ =\ W\ \times\ (50\ −\ 30)\)
\(⇒\ 40\ \times\ 25\ =\ W\ \times\ 20\ =\ 50\ gf\)
Weight of the metre scale \(=\ 50\ gf\)
(ii) To maintain equilibrium, the fulcrum F, is shifted towards 0 cm mark.
Question 23
(i) Define moment of force.
(ii) Write the relationship between the SI and CGS unit of moment of force. [ICSE 2020]
Answer:
(i) Moment of force: The moment of a force defined as the product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force.
(ii) Relationship between the SI unit and CGS unit of moment of force:
\(1\ Nm\ =\ 10^7\ dyne\ cm\)
Question 24
(i) With reference to the direction of action how does a centripetal force differ from a centrifugal force during uniform circular motion.
(ii) Is centrifugal force the form of reaction of centripetal force?
(iii) Compare the magnitude of centripetal and centrifugal force. [ICSE 2020]
Answer:
(i) Centripetal force acts towards the center of the circular path, while centrifugal force acts away from the center.
(ii) No, centrifugal force is not the force of reaction of the centripetal force.
(iii) The magnitude of the centripetal and the centrifugal force are equal but their direction are opposite to each other.
Question 25
Choose the correct answer:
Clockwise moment produced by a force about a fulcrum is considered to be: [ICSE 2023]
(a) Positive (b) Negative
(c) Zero (d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Negative
Question 26
(i) What is the position of the centre of gravity of a triangular lamina?
(ii) When this triangular lamina is suspended freely from any one vertex, what is the moment of force produced by its own weight in its rest position? [ICSE 2023]
Answer:
(i) The centre of gravity for a triangular lamina is at the point of intersection of the medians.
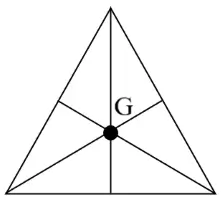
(ii) When the triangular lamina is suspended freely from any vertex, the moment of force produced by its own weight in its rest position is zero, because the centre of gravity lies vertically below the point of suspension, causing no turning effect.
Question 27
(i) The diagram shows wheel O pivoted at point A. Three equal forces \(F_1,\ F_2\) and \(F_3\) act at point B on the wheel.
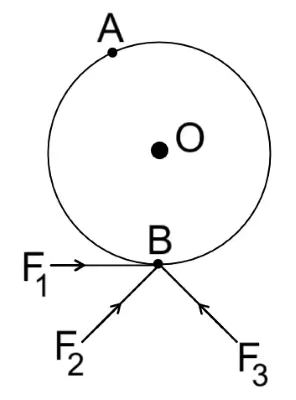
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (i). [ICSE 2023]
Answer:
(i) Force \(F_1\) produces the maximum moment.
(ii) Force \(F_1\) produces the maximum moment because it has the largest perpendicular distance from the pivot point A to its line of action.
Question 28
Choose the correct answer:
A door lock is opened by turning the lever (handle) of length \(0.2\ m\). If the moment of force produced is \(1\ Nm\), then the minimum force required is : [ICSE 2024]
(a) 5 N (b) 10 N
(c) 20 N (d) 0.2 N
Answer:
(a) 5 N
Question 29
When a stone tied to a string is rotated in a horizontal plane, the tension in the string provides _________ force necessary for circular motion. [ICSE 2024]
Answer:
When a stone tied to a string is rotated in a horizontal plane, the tension in the string provides centripetal force necessary for circular motion.
Question 30
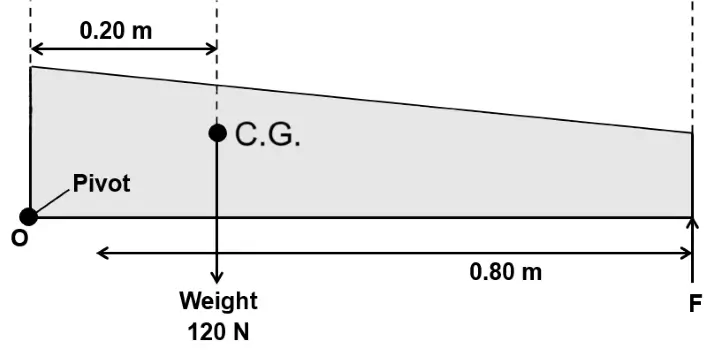
A non uniform beam of weight \(120\ N\) pivoted at one end is shown in the diagram below. Calculate the value of \(F\) to keep the beam in equilibrium. [ICSE 2024]
Answer:
Given,
Weight of the beam, \(W\ =\ 120\ N\)
Distance from the pivot to the center of gravity (C.G.) \(=\ 0.20\ m\)
Distance from the pivot to the point where force F is applied \(=\ 0.80\ m\)
According to equilibrium condition,
Anticlockwise moment \(=\) Clockwise moment
\(⇒\ 120 \times 0.20\ =\ F \times 0.80\)
\(⇒\ F\ = \frac{120\ \times\ 0.20}{0.80}\)
\(⇒\ F\ = \frac{24}{0.80}\ = 30\ N\)
The value of \(F\) required to keep the beam in equilibrium is \(30\ N\).
Question 30
(a) Define Centre of Gravity.
(b) A hollow ice cream cone has height \(6\ cm\).
(i) Where is the position of its centre of gravity from the broad base?
(ii) Will its position change when it is filled completely with honey? Write Yes or No. [ICSE 2024]
Answer:
(a) Centre of gravity: The centre of gravity of a body is defined as the point about which the algebraic sum of moments of weights of particles constituting the body is zero and the entire weight of the body is to act at this point.
(b) (i) Height of hollow ice cream cone \(=\ 6\ cm\)
Position of CG \(=\ \frac h3\ =\ \frac63\ =\ 2\ cm\)
(ii) Yes, now cone is a Solid cone. So, the position of the new center of gravity from the base will be \(\frac{h}{4}\ cm\) i.e., \(\frac64\ =\ 1.5\ cm\) from the base of the cone.
Question 31
Choose the correct answer:
A body is acted upon by two equal and opposite forces, that are NOT along the same straight line.
The body will: [ICSE 2025]
(a) remain stationary
(b) have only rotational motion
(c) have only rectilinear motion
(d) have both rectilinear and rotational motion
Answer:
(b) have only rotational motion
Question 32
Choose the correct answer:
In uniform circular motion the centrifugal force acts __________. [towards the centre / away from the centre /along the tangential direction] [ICSE 2025]
Answer:
In uniform circular motion the centrifugal force acts away from the centre.
Question 33
A non-uniform kite is hanging freely from the branch of a tree as shown. Study the figure and answer the following: [ICSE 2025]
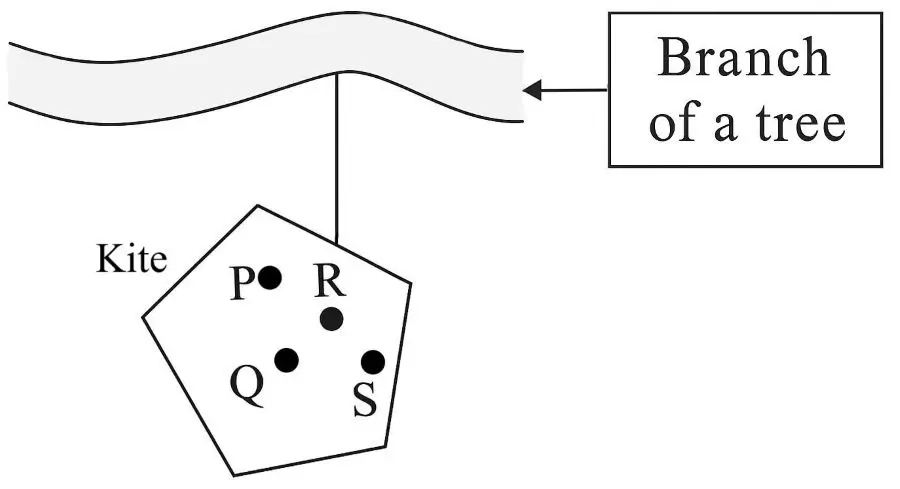
(a) Fill in the blank:
______ (P, Q, R or S) as the most probable position of its centre of gravity.
(b) Support your answer to (a) with a reason.
Answer:
(a) Q as the most probable position of its centre of gravity.
(b) Reason: When an object hangs freely, its center of gravity lies along the vertical line passing through the point of suspension.
Download Force – Previous Year Questions PDF
You can download our free Force – Previous Years’ Questions with answers (PDF format) to test your understanding.
Pro Tips for Exam Preparation
- Focus on numerical and reasoning questions – they carry higher weightage.
- Practice diagrams neatly with labels – common in 3-mark and 4-mark questions.
- Refer to Selina Concise Physics and ICSE sample papers for model answers.
- Use a formula sheet for quick revision of moment of force, torque, and lever rules.
You can also visit :
| ICSE Class 10 Physics |
| ICSE Class 10 Chemistry |
| ICSE Class 10 Mathematics |
ICSE Class 10 Physics Important Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 1 – Force Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 2 – Work, Energy and Power Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 3 – Machines Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 5 – Refraction through Lens Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 6 – Spectrum Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 7 – Sound Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 8 – Current Electricity Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 9 – Electrical Power and Household Circuits Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 10 – Electro-magnetism Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 11 – Calorimetry Previous Year Questions
- Chapter 12 – Radioactivity Previous Year Questions

