Introduction
In continuation of Spectrum Chapter (Selina Solutions Class 10 Physics), Exercise 6(B) focuses on applications of the spectrum, properties of radiations, and their uses. Practicing these solutions will help students gain conceptual clarity and secure excellent marks in exams.
ICSE Physics Spectrum Exercise 6(B) – Key Topics
- Properties of infrared, ultraviolet, and X-rays
- Uses of different types of radiation
- Precautions while using harmful radiations
- Daily life applications of spectrum
(A) Multiple Choice Type
(Choose the correct answer from the options given below).
Question 1
When an electromagnetic wave passes from one medium to the other, which property remains unchanged ?
(a) speed (b) wavelength
(c) direction of travel (d) frequency
Answer:
(d) frequency
Explanation:
The speed and wavelength of light change when it moves from one medium to another (due to refraction). Frequency always remains constant because the source of the wave doesn’t change.
Question 2
Two waves A and B have wavelengths \(0.001\ Å\) and \(9000\ Å\) respectively. The waves A and B are:
(a) Gamma wave and ultraviolet wave respectively.
(b) Microwave and infrared wave respectively.
(c) Radiowave and gamma wave respectively.
(d) Gamma wave and infrared wave respectively.
Answer:
(d) Gamma wave and infrared wave respectively
Explanation:
- \(0.001\ Å =1 \times 10^{-12}\) → belongs to gamma ray region.
- \(9000\ Å =9 \times 10^{-7}\) → belongs to infrared region.
Question 3
The correct arrangement of the following radiations in an increasing order of their wavelengths is :
X-rays, infrared rays, gamma rays, microwaves.
(a) gamma rays, infrared rays, X-rays, microwaves
(b) gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves, infrared rays
(c) gamma rays, X-rays, infrared rays, microwaves
(d) X-rays, gamma rays, infrared rays, microwaves
Answer:
(c) gamma rays, X-rays, infrared rays, microwaves
Explanation:
Order of electromagnetic spectrum by increasing wavelength:
Gamma rays → X-rays → Ultraviolet → Visible → Infrared → Microwaves → Radio waves.
Question 4
A radiation P is focused by a proper device on the bulb of a thermometer. Mercury in the thermometer shows a rapid increase. The radiation P is :
(a) infrared radiation
(b) visible light
(c) ultraviolet radiation
(d) X-rays
Answer:
(a) infrared radiation
Explanation:
Infrared radiation produces strong heating effect, which quickly raises the temperature of mercury in a thermometer.
Question 5
The most energetic electromagnetic radiations are :
(a) Microwaves
(b) ultraviolet waves
(c) X-rays
(d) gamma rays
Answer:
(d) gamma rays
Explanation:
Energy of radiation is inversely proportional to wavelength. Gamma rays have the shortest wavelength, hence maximum energy.
Question 6
Column X shows the kinds of electromagnetic waves and column Y shows their applications.
| Column X | Column Y |
| (A) Infrared rays | (i) in remote-controlled gadgets |
| (B) Radio waves | (ii) for transmission |
| (C) X-rays | (iii) for detection of bone fractures |
| (D) Ultraviolet rays | (iv) absorption by atmospheric ozone layer |
Choose the correct pairing :
(a) A – (i), B – (ii), C – (iii), D – (iv)
(b) A – (iv), B – (iii), C – (ii), D – (i)
(c) A – (i), B – (ii), C – (iv), D – (iii)
(d) A – (iii), B – (ii), C – (i), D – (iv)
Answer:
(a) A – (i), B – (ii), C – (iii), D – (iv)
Explanation:
The correct pairing is :
| Column X | Column Y |
| (A) Infrared rays | (i) in remote-controlled gadgets |
| (B) Radio waves | (ii) for transmission |
| (C) X-rays | (iii) for detection of bone fractures |
| (D) Ultraviolet rays | (iv) absorption by atmospheric ozone layer |
(B) Very Short Questions
Question 1
(a) Arrange the following radiations in the order of their increasing wavelength:
X-rays, infrared rays, radio waves, gamma rays and micro waves.
(b) Name the radiation which is used for satellite communication?
Answer:
(a) Arrange in increasing wavelength:
Gamma rays < X-rays < Infrared rays < Microwaves < Radio waves
(b) Radiation used for satellite communication: Microwaves
Question 2
A wave has a wavelength of \({10}^{-3}\) nm.
(a) Name the wave.
(b) State it’s one property different from light.
Answer:
(a) The wave which has a wavelength of \({10}^{-3}\) nm is gamma rays.
(b) Property: Very high penetrating power
Question 3
(a) Name the high energetic invisible electromagnetic wave which helps in the study of the structure of crystals.
(b) State one more use of the wave named in part (a).
Answer:
(a) X-rays are used in the study of atomic arrangement in crystals as well as in complex molecules.
(b) Other use: Medical imaging (X-ray photography)
Question 4
State the name and the range of wavelength of the invisible electromagnetic waves beyond the red end of visible spectrum.
Answer:
The invisible electromagnetic waves beyond the red end of visible spectrum are called the infrared (or heat) radiations.
Range of wavelength of infrared radiations is 8000 Å to 107 Å.
Question 5
Give the range of wavelength of the electromagnetic waves visible to us.
Answer:
The range of wavelength of the electromagnetic waves visible to us is 4000 Å to 8000 Å.
Question 6
Name the region just beyond
(i) the red end and
(ii) the violet end, of the spectrum.
Answer:
(i) Just beyond red end: Infrared rays
(ii) Just beyond violet end: Ultraviolet rays
Question 7
Name the radiation which can be detected by (a) a thermopile (b) a solution of silver chloride.
Answer:
(a) Detected by thermopile: Infrared rays
(b) Detected by silver chloride solution: Ultraviolet rays
Question 8
Name the radiations of wavelength just
(a) longer than \(8\times{10}^{-7}\ m\),
(b) shorter than \(4\times{10}^{-7}\ m\)
Answer:
(a) wavelength longer than \(8\times{10}^{-7}\ m\) : infrared
(b) wavelength shorter than \(4\times{10}^{-7}\ m\) : Ultraviolet
Question 9
Name the material of prism required for obtaining the spectrum of (a) ultraviolet light, (b) infrared radiations.
Answer:
(a) Prism material for UV light: Quartz
(b) Prism material for IR radiation: Rock salt (NaCl)
Question 10
Name the radiations which are absorbed by the green house gases in the earth’s atmosphere.
Answer:
Radiations absorbed by greenhouse gases: Infrared rays
(C) Short Questions
Question 1
(a) Give a list of at least five radiations, in the order of their increasing wavelength, which make up the complete electromagnetic spectrum.
(b) Name the radiation mentioned by you in part (a) which has the highest penetrating power.
Answer:
(a) Order of increasing wavelength :
Gamma rays < X-rays < Ultraviolet < Visible light < Infrared < Microwaves < Radio waves
(b) Highest penetrating power: Gamma rays
Question 2
A wave has wavelength . (a) Name the wave. (b) State it’s speed in vacuum. (c) State it’s one use.
Answer:
(a) The electromagnetic wave having wavelength \(50\ Å\) is X-ray.
(b) Speed in vacuum \(=\ 3\times{10}^8\ {ms}^{-1}\)
(c) X-ray waves are used for the detection of fracture in bones, teeth etc (i.e., radiography).
Question 3
Name three radiations and their wavelength range which are invisible and beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum.
Answer:
The three radiations which are invisible and beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum:
| Radiation | Wavelength (nm) |
| (i) Ultraviolet rays | 10 – 400 |
| (ii) X-rays | 0.01 – 10 |
| (iii) Gamma rays | below 0.01 |
Question 4
What do you understand by the invisible spectrum?
Answer:
The invisible spectrum is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum beyond the visible range. It includes ultraviolet rays (shorter wavelength than violet) and infrared rays (longer wavelength than red), which the human eye cannot see.
Question 5
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with (a) ultraviolet rays, (b) visible light, and (c) infrared rays.
Answer:
(a) Ultraviolet rays : \(100\ Å- 4000\ Å \left(10\ nm\ -\ 400\ nm\right)\)
(b) Visible light : \(4000\ Å- 8000\ Å \left(400\ nm\ -\ 800\ nm\right)\)
(c) Infrared rays : \(8000\ Å- 10^7\ Å \left(800\ nm\ -\ 10^6\ nm\right)\)
Question 6
Name two electromagnetic waves of wavelength smaller than that of violet light. State one use of each.
Answer:
- Ultraviolet rays : Used for sterilization (kills germs).
- X-rays : Used for medical imaging of bones.
Question 7
Give one use each of (a) microwaves, (b) ultraviolet radiations, (c) infrared radiations, and (d) gamma rays.
Answer:
(a) Microwaves : Used in radar and cooking (microwave ovens).
(b) Ultraviolet radiations : Sterilization of surgical instruments.
(c) Infrared radiations : Used in remote controls and night vision devices.
(d) Gamma rays : Used to treat cancer (radiotherapy).
Question 8
Name the waves (a) of lowest wavelength, (b) used for taking photographs in dark, (c) produced by the changes in the nucleus of an atom, (d) of wavelength nearly 0.1 nm
Answer:
(a) Of lowest wavelength : Gamma rays
(b) Used for taking photographs in dark : Infrared rays
(c) Produced by changes in the nucleus of an atom : Gamma rays
(d) Of wavelength nearly 0.1 nm : X-rays
Question 9
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively. (a) Name the two waves. (b) Compare the speeds of these waves when they travel in vacuum.
Answer:
(a) Wave A = Gamma rays; Wave B = Infrared rays
(b) Both travel with the same speed in vacuum, i.e. \(3\ \times\ {10}^8\ m/s\).
Question 10
Name two sources, each of infrared radiations and ultraviolet radiations.
Answer:
- Infrared sources: (i) Sun, (ii) Electric heaters
- Ultraviolet sources: (i) Sun, (ii) Mercury vapor lamp
Question 11
Name two properties of ultraviolet radiations which are similar to the visible light and two which differ from visible light.
Answer:
Similar :
- Travel in straight lines
- Obey laws of reflection and refraction
Different :
- Not visible to the eye,
- Have higher energy and shorter wavelength
Question 12
Mention two properties of infrared radiations which are similar to the visible light and two which differ from visible light.
Answer:
Similar :
- Travel in straight lines,
- Obey reflection and refraction laws
Different :
- Not visible to the eye
- Produce heating effect
Question 13
State one harmful effect each of the (a) ultraviolet and (b) infrared radiations.
Answer:
(a) Ultraviolet radiations : Cause sunburn and skin cancer
(b) Infrared radiations : Can damage the eye lens (cataract)
Question 14
Give reason for the following:
(i) Infrared radiations are used for photography in fog.
(ii) Infrared radiations are used for signals during the war.
(iii) The photographic darkrooms are provided with infrared lamps.
(iv) A rock salt prism is used instead of a glass prism to obtain the infrared spectrum.
(v) A quartz prism is required for obtaining the spectrum of the ultraviolet light.
(vi) Ultraviolet bulbs have a quartz envelope instead of glass.
Answer:
(i) Infrared radiations are used for photography in fog – They can penetrate through fog and mist.
(ii) Infrared radiations are used for signals during war – They are invisible and provide secrecy.
(iii) The photographic darkrooms are provided with infrared lamps – They do not affect photographic plates/films.
(iv) A rock salt prism is used instead of a glass prism to obtain infrared spectrum – Glass absorbs infrared rays, rock salt does not.
(v) A quartz prism is required for obtaining ultraviolet spectrum – Glass absorbs ultraviolet rays, quartz transmits them.
(vi) Ultraviolet bulbs have a quartz envelope instead of glass – Glass absorbs ultraviolet rays, quartz allows them to pass.
Question 15
Radiations from the sun fall on a prism and suffer dispersion. Three thermometers are kept on which the radiations after dispersion are made to fall as shown in the figure given below. Which thermometer would show a higher reading ? Give a reason for your answer.
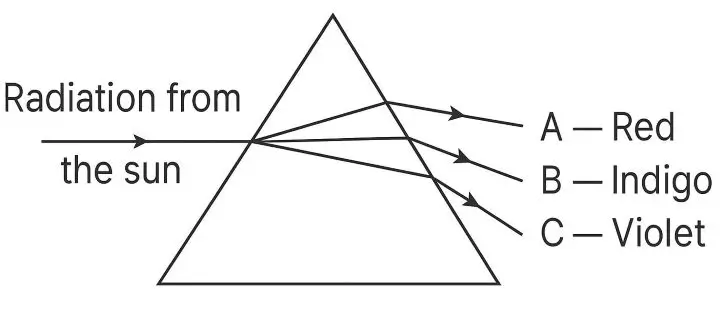
Answer:
The thermometer at A (Red) will show the highest reading.
Reason:
Red light has the longest wavelength and the least frequency among the visible spectrum. Because of this, it is less scattered and carries more heat energy compared to violet or indigo light. That’s why the thermometer placed in the red region of the spectrum records a higher temperature.
So, Thermometer A (Red) → highest reading.
(D) Long Questions
Question 1
What are infrared radiations? How are they detected? State one use of these radiations.
Answer:
Infrared radiations: Infrared (IR) radiations are invisible rays beyond the red end of the visible spectrum. Their wavelength is longer than that of red light but shorter than microwaves. They are mainly responsible for the heat we feel from the sun or any hot object.
Detection:
They can be detected by a thermometer (rise in temperature), photographic films, or special detectors like thermopiles.
One use:
They are used in night vision cameras (to see in the dark), or in TV remote controls, or for drying and heating purposes.
Question 2
What are ultra violet radiations? How are they detected? State one use of these radiations.
Answer:
Ultraviolet (UV) radiations:
Ultraviolet radiations are invisible rays that lie just beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum. They have shorter wavelengths than visible light but longer than X-rays.
Detection:
They can be detected by their effect on photographic plates, by causing fluorescence in certain substances, or by using photoelectric cells.
One use:
They are used for sterilizing medical instruments because UV rays kill germs and bacteria.
(E) Numericals
Question 1
An electromagnetic wave has a frequency of 500 MHz and a wavelength of 60 cm.
(a) Calculate the speed of the wave.
(b) Name the medium through which it is travelling.
Answer:
(a) Given,
Frequency, \(f=500\ MHz=500\times\ {10}^6\ Hz\ =\ 5\times\ {10}^8\ Hz\)
Wavelength, \(\lambda=60\ cm\ =\ 0.60\ m\)
As we know,
Velocity of wave (c) = frequency (f) x wavelength (λ)
\(\Rightarrow\ c=\ \left(5\times\ {10}^8\ Hz\right)\times\ \left(0.60\ m\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\ c=3\times\ {10}^8\ m/s\)
Hence, The speed of the wave is \(3\times\ {10}^8\ m/s\).
(b) The electromagnetic wave is travelling through air.
Question 2
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å . Calculate it’s frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
Answer:
Given:
Wavelength of X-rays, \(\lambda=0.01\ Å\)
\(\lambda=0.01\ \times{10}^{-10}\ m=\ {10}^{-12}\ m\)
\(c=\ 3\times\ {10}^8 m/s\)
The frequency (f) is given by:
\(f=\frac{c}{\lambda}\)
\(f=\frac{3\times\ {10}^8\ }{{10}^{-12}}\)
\(f=3\times\ {10}^{20}\ Hz\)
Hence, Frequency of X-rays \(=3\times\ {10}^{20}\ Hz\).
Assumption: X-rays are traveling in vacuum/air, so \(c=3\times\ {10}^8\ m/s\).
Free PDF Download – Spectrum Exercise 6(B) Solutions
Download ICSE Class 10 Physics Selina Solutions Chapter 6 Spectrum Exercise 6(B) PDF for free and revise offline anytime.

